在 昨天 Day 16 (RAG) 的 Demo 裡,眼尖的朋友可能會發現其實我們已經用到了一些 Tools 的概念 —— 把檢索包裝成工具,讓模型可以在需要時自行呼叫。
回顧更早的 核心篇 Day 6 (Tool Use),我們則示範了工具的基本概念:讓模型不只是回話,還能透過工具完成任務。
不過,以往為了方便展示與說明,許多工具都是「固定回傳值」或「簡單規則」,例如輸入「雨天」就回傳「去博物館」。
今天,我們要更進一步 —— 運用 LangChain v1.0 提供的工具系統,來做出真正「可用」的工具。
這次我們會接上 AccuWeather API,讓模型真的能查維也納的即時天氣,從 Demo 變成真正能「動手做事」的智慧助理。
在 LangChain v1.0 中,工具的設計可以透過幾個核心組件來完成:
@tool,把一個函式變成模型可安全呼叫的「能力」。ToolNode 來統一處理工具的呼叫與錯誤。create_agent(),把模型和工具結合起來,讓 AI 能根據情境自行決定是否要動用工具。接下來,我們就來逐一看看這些元件的實際應用。
@tool用 @tool 裝飾器把函式轉換成 Tool。
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def search_database(query: str, limit: int = 10) -> str:
"""在客戶資料庫中搜尋紀錄。
Args:
query: 搜尋關鍵字
limit: 最大回傳筆數
"""
return f"Found {limit} results for '{query}'"
這樣模型就能以結構化方式呼叫 search_database,而不是瞎猜字串。
ToolNodeToolNode 是 LangGraph 提供的組件,用來處理 Agent 執行過程中的工具呼叫。
它支援:
from langchain.agents import ToolNode
tool_node = ToolNode(
tools=[search_database],
handle_tool_errors=True
)
如果工具拋出錯誤,Agent 仍能繼續回應,不會中斷。
create_agent()最後,把 LLM + ToolNode + Prompt 組合成 Agent。
這樣模型就能:
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.agents import create_agent
llm = init_chat_model("gemini-2.5-flash", model_provider="google_genai")
agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=tool_node,
system_prompt="你是一位資料查詢助理。"
)
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "幫我搜尋名字含 Alice 的紀錄"}]
})
這就是「思考 → 工具呼叫 → 工具結果 → 最終回答」的完整循環。
接下來我們實際接上 AccuWeather API:
讓模型能查維也納的即時天氣。
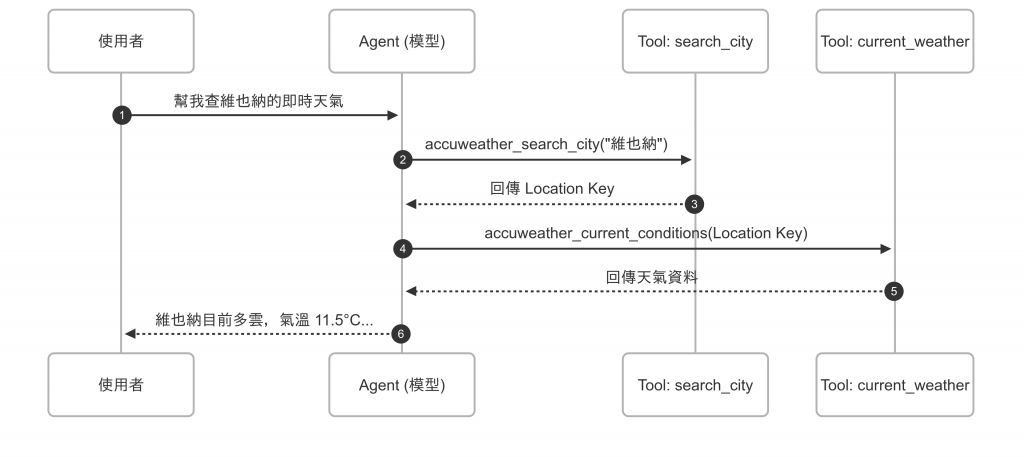
圖:維也納天氣查詢流程示意圖。使用者輸入問題後,Agent 先透過 accuweather_search_city 工具找到對應的 Location Key,再呼叫 accuweather_current_conditions 查詢即時天氣,最後由 Agent 整合結果並以自然語言回覆使用者。這個過程展示了模型如何在對話中動態決定並運用工具完成任務。
在開始寫程式之前,需要先去 AccuWeather 開發者網站 申請 API Key。
AccuWeather 提供免費額度(包含一定數量的 API 呼叫),足夠我們做測試與開發使用。
申請好 API Key 後,記得將它設定成環境變數,例如:
export ACCUWEATHER_API_KEY="你的_API_KEY"
這樣程式就能正確呼叫 AccuWeather API。
pip install -q --pre -U langchain
pip install -q -U langchain-google-genai
import os, requests
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import ToolNode, create_agent
API_KEY = os.getenv("ACCUWEATHER_API_KEY")
if not API_KEY:
raise ValueError("請先設定 ACCUWEATHER_API_KEY 環境變數")
# --------- 定義工具 ---------
@tool
def accuweather_search_city(city: str, country_code: str = "AT") -> dict:
"""用 AccuWeather 搜尋城市並回傳 Location Key。"""
url = "https://dataservice.accuweather.com/locations/v1/cities/search"
params = {"apikey": API_KEY, "q": city, "language": "zh-tw"}
r = requests.get(url, params=params, timeout=10)
r.raise_for_status()
data = r.json()
if not data:
return {"error": f"找不到城市:{city}"}
return data[0]
@tool
def accuweather_current_conditions(location_key: str) -> dict:
"""查詢指定 Location Key 的即時天氣。"""
url = f"https://dataservice.accuweather.com/currentconditions/v1/{location_key}"
params = {"apikey": API_KEY, "language": "zh-tw", "details": "true"}
r = requests.get(url, params=params, timeout=10)
r.raise_for_status()
data = r.json()
return data[0] if data else {"error": f"查不到天氣:{location_key}"}
tools = [accuweather_search_city, accuweather_current_conditions]
# --------- 初始化模型 ---------
llm = init_chat_model("gemini-2.5-flash", model_provider="google_genai", temperature=0)
# --------- 建立 ToolNode + Agent ---------
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools, handle_tool_errors=True)
agent = create_agent(
model=llm,
tools=tool_node,
system_prompt="你是專業氣象助理。查詢天氣時,先用 accuweather_search_city (city 傳入中文即可) 找 Location Key,再用 accuweather_current_conditions。"
)
# --------- 執行 ---------
resp = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "幫我查維也納的即時天氣"}]
})
print("\n=== 對話歷程 ===")
for m in resp["messages"]:
role = m.__class__.__name__
print(f"[{role}] {getattr(m, 'content', '') or getattr(m, 'tool_calls', '')}")
print("\n=== 模型最終回答 ===")
print(resp["messages"][-1].content)
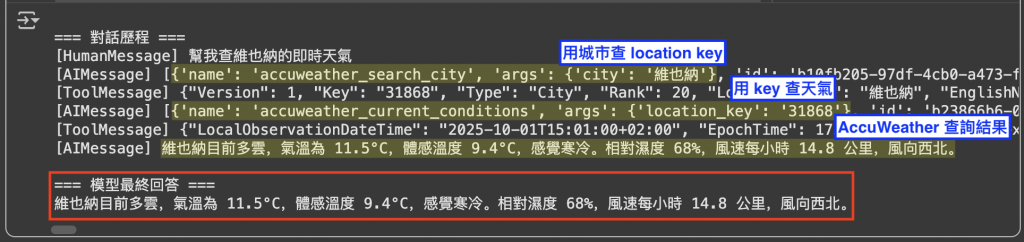
圖:維也納天氣查詢 Demo 執行結果。模型先透過工具查城市代碼,再以代碼查即時天氣,最後組合成自然語言回答。使用者從中獲得具體可用的氣象資訊。
在這個 Demo 中,我們可以清楚看到模型如何 逐步運用工具完成任務:
accuweather_search_city 工具,根據使用者輸入的城市名稱找到對應的 Location Key。這一步確保後續查詢有正確的識別碼。accuweather_current_conditions 工具,帶入 Location Key 呼叫 AccuWeather API,取得完整的氣象資料(包含氣溫、體感溫度、濕度、風速等)。結果不只是「文字上的推測」,而是真正串接外部資料來源,讓回答帶有 即時性與可靠性。
這正是 Tool Use 的價值:讓模型不再只是憑空回答,而是能透過工具實際完成任務。
今天我們探討了 LangChain v1.0 的 Tools 元件:
@tool 讓我們能把一個函式變成 AI 可安全呼叫的能力ToolNode 負責在推理過程中處理工具的呼叫與錯誤create_agent() 則把模型與工具真正結合,讓 AI 能根據情境自主決定是否需要動手透過「維也納天氣小幫手」這個 Demo,我們看到 AI 不再只是單純回答,而是能 實際完成任務。這次不是模擬,而是真正串接 API,讓回覆具備 即時性與實用性。
相較於以往為了展示流程而設計的「固定回傳值」或「簡單規則」工具,今天的實作更進一步,讓 AI Agent 真正接上外部世界,展現了實戰級的價值。
明天,我們會進一步探索 MCP (Model Context Protocol) —— 看看如何讓工具不只是「能用」,而是「更有效率、更好管理」。有了今天的基礎,明天將會是 從工具到協作 的新篇章。

圖:布拉格舊城廣場的天文鐘(Astronomical Clock)。這座中世紀的傑作,不只是一個鐘,而是凝聚了天文、曆法與藝術的智慧,更象徵著多重知識的協奏 —— 正如 Tool Use,讓 AI 不再只是「單一回答」,而是能調度多種能力,共同運作。(攝影:作者自攝)
