昨天提到 Prompt function calling 跟 FC (native) 的差別。最後決定要走 FC,因為簡單、省 token,而且在 agentic domain 上分數直接碾壓。
今天就來實際分享一下我怎麼改 Reasoning state,把 open ai 的 FC 用進來。
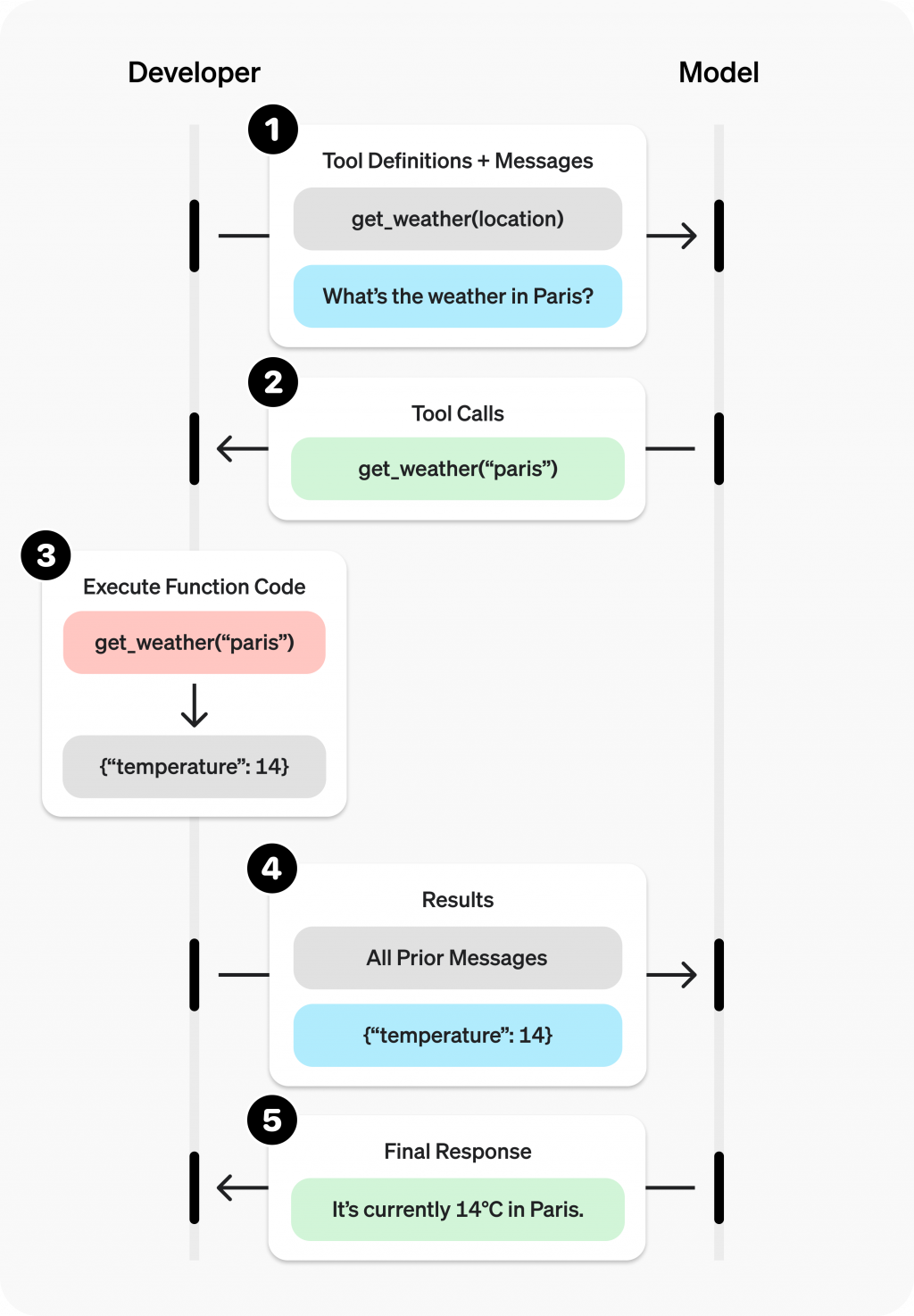
拿 openai 的圖來解釋,反正 function calling 就是透過提供固定 format 的 tools,讓 llm 根據prompt去選擇要選擇使用哪些 tools。
由於之後還是打算把 mcp server 帶進來,所以先理解一下 MCP tool list 的格式
首先要解釋一下,MCP (multi-component protocol) 的 tool list 跟 open ai 的 tools 參數格式其實不一樣。
MCP tool list:通常會包含比較多 metadata,例如:
{
name: string; // Unique identifier for the tool
description?: string; // Human-readable description
inputSchema: { // JSON Schema for the tool's parameters
type: "object",
properties: { ... } // Tool-specific parameters
}
}
ref: https://modelcontextprotocol.info/docs/concepts/tools/
可以看到它的 schema key 是 inputSchema。
OpenAI tools 格式:
定義: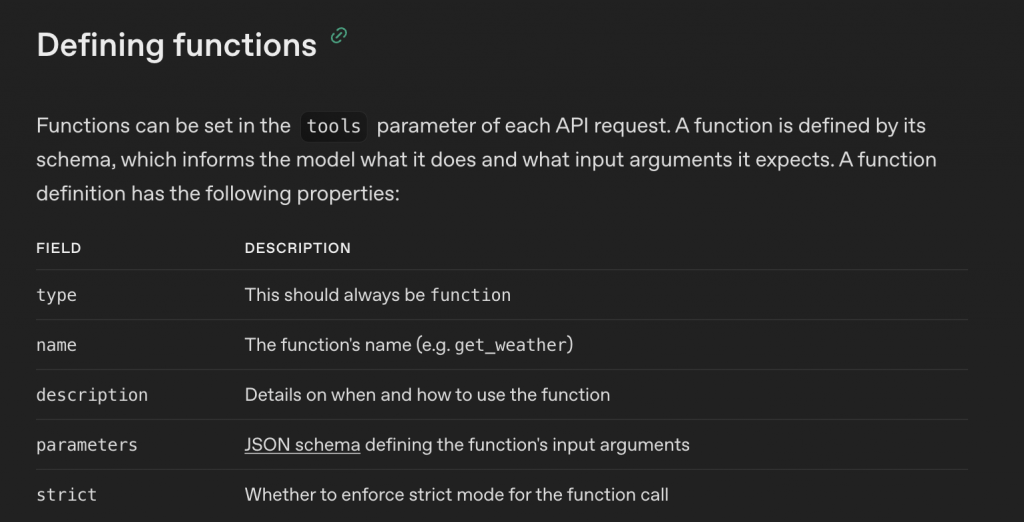
小小例子
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Retrieves current weather for the given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City and country e.g. Bogotá, Colombia"
},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "Units the temperature will be returned in."
}
},
"required": ["location", "units"],
"additionalProperties": false
},
"strict": true
}
ref: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling
是有看到一些 adapter 的 repo,但感覺有點小眾 就不貼了。
看樣子是有人想要整合 function 的格式呢XD
Unified Tool Integration for LLMs: A Protocol-Agnostic Approach to Function Calling
接下來就是改 code。
我寫了一個 get_response function,用來呼叫 open ai,然後 parse 出工具調用:
async def get_response(model_name: str, messages: list[Message], tools: list[dict] | None = None):
respone = await client.chat.completions.create(model=model_name, messages=messages, tools=tools)
tool_raw_infos = respone.choices[0].message.tool_calls
tool_infos = (
[
{"name": tool_call.function.name, "args": json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)}
for tool_call in tool_raw_infos
if tool_call.type == "function"
]
if tool_raw_infos
else None
)
return (
respone.choices[0].message.content,
tool_infos,
)
然後在 ReasoningState 裡就就改呼叫 get_response
class ReasoningState(State):
async def run(self, memory: "Memory") -> AsyncIterator[str]:
messages = await get_messages(memory)
content, tools = await get_response(
model_name=REASONING_MODEL, messages=messages, tools=mcp_to_openai_tools(memory.list_tools())
)
if content:
for chunk in content:
yield chunk
await memory.update([Message(role=Role.ASSISTANT, content=content)])
yield str(tools)
if tools:
memory.next_actions = [Action(**tool) for tool in tools]
async def next_state(self, memory: "Memory") -> Enum:
if memory.next_actions:
return ReAct.ACTION
return ReAct.ANSWER
答案是 Yes。
tools,裡面是 function + parameters。tool_choice,定義方式又不一樣。function_declarations。明天真的就會跑跑看 toolhop dataset,看 react 的分數了...
