廣度優先搜尋 (Breadth-first Search),也稱之為寬度優先搜尋。和深度優先搜尋不同的是,深度優先是透過函數的遞迴來延伸運算,而廣度優先則是透過「一層一層」擴展的方式來搜尋。
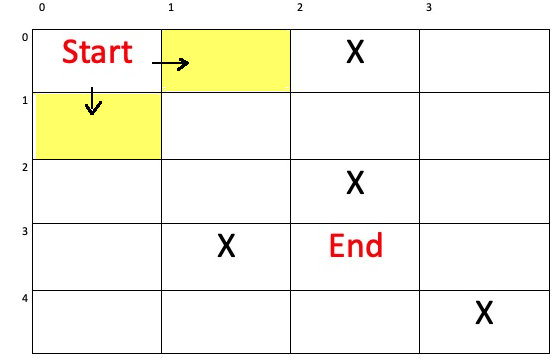
我們用一個圖來講解。我們要從起點走到終點,一格一格的走,但有上下左右四個方向,所以需要一層一層的擴展(用不同顏色表示)。而在程式碼的運算上,是將每個擴展的點以及步數分別加入到x、y座標和步數的佇列,最後在到達終點的時候輸出。
Start = 起點,End = 終點,X = 障礙物。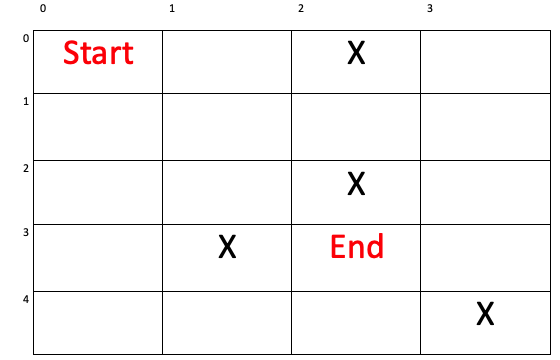
| step(步數) | 0 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x(縱座標) | 0 | ||||||||
| y(橫座標) | 0 | ||||||||
 |
|||||||||
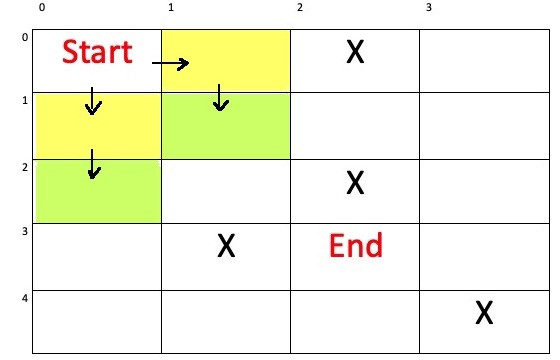
| step(步數) | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| x(縱座標) | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||
| y(橫座標) | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||
 |
|||||||||
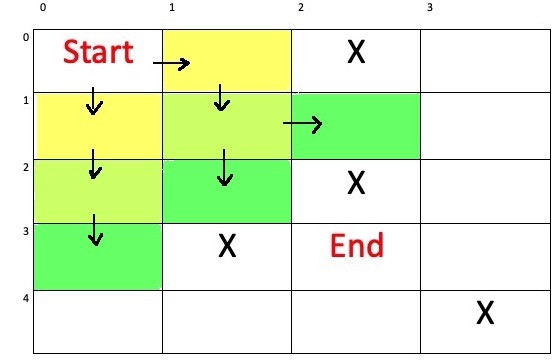
| step(步數) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| x(縱座標) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| y(橫座標) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
 |
|||||||||
| step(步數) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| x(縱座標) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| y(橫座標) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
class note():
def __init__(self, n, m):
self.x = [0] * n * m # 縱座標
self.y = [0] * n * m # 橫座標
self.f = [0] * n * m # 父親在佇列中的編號
self.s = [0] * n * m # 步數
# 此為迷宮,0 = 空格,1 = 障礙
maze = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# 設定迷宮大小
n = len(maze)
m = len(maze[0])
# 設一個陣列,用來標記走過的座標
book = []
for i in range(n):
book.append([0] * m)
# 設定起訖點
startx = 0
starty = 0
endx = 3
endy = 2
# 定義一個表示走的方向的陣列
next = [[0, 1], # 向右走
[1, 0], # 向下走
[0, -1], # 向左走
[-1, 0]] # 向上走
# 佇列初始化
head = 0
tail = 0
# 往佇列插入迷宮入口座標
que = note(n, m)
que.x[tail] = startx
que.y[tail] = starty
que.f[tail] = 0
que.s[tail] = 0
tail += 1
book[startx][startx] = 1
flag = 0 # 用來標記是否到達目標,0 = 未到,1 = 到達
# 當佇列不為空的迴圈
while(head < tail):
# 列舉4個方向
for i in range(4):
# 計算下一個座標
tx = que.x[head] + next[i][0]
ty = que.y[head] + next[i][1]
# 判斷是否越界
if tx < 0 or tx > n-1 or ty < 0 or ty > m-1 :
continue
# 判斷是否是障礙物或者已經走過
if maze[tx][ty] == 0 and book[tx][ty] == 0 :
book[tx][ty] = 1 # 標記為已走過
# 插入新的點到佇列中
que.x[tail] = tx
que.y[tail] = ty
que.f[tail] = head
que.s[tail] = que.s[head] + 1 # 步數是父親步數+1
tail += 1
# 若到訖點,停止擴展退出迴圈
if tx == endx and ty == endy :
flag = 1
break
if flag == 1 :
break
head += 1 # 當一個擴展結束後,要head++才能對後面的點再進行擴展
# 列印佇列中末尾最後一個點(訖點)的步數,但tail是指向佇列尾的下一個位置,所以要-1
print(que.s[tail-1])
print(que.x)
print(que.y)
擴展的路徑圖(佇列)。
step = 7
x = [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 4, 2, 0, 4, 3, 4, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0]
y = [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 3, 0, 3, 3, 1, 3, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0]
