介紹Kubernetes到現在我們都還沒提及到Kubernetes cluster是如何去區分不同使用者與其所屬全限,但在講述這些之前我必須先提及一個東西,那就是namespace命名空間。
何謂namespace命名空間呢? 其實我們一直在使用,當我們在不指定namespace的情況下會預設為default namespace。Namespace命名空間提供了抽象群集的概念。我們能根據專案的不同、商業邏輯不同或是其他原由將原本擁有所有實體資源的Kubernetes cluster切分成n個virtual cluster,也就是namespace。
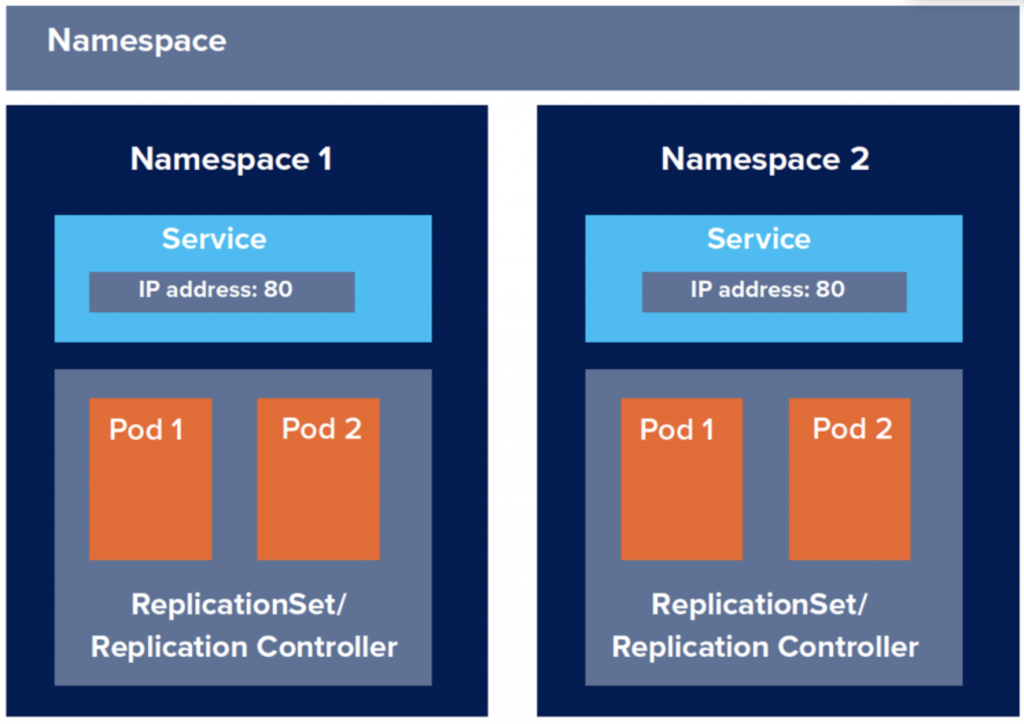
這邊我先透過kubectl get ns 來介紹幾個較為特殊的namespace
$ kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 17d
kube-node-lease Active 17d
kube-public Active 17d
kube-system Active 17d
kubernetes-dashboard Active 15d
namespace具有以下幾個特點:
kubectl create namespace <namespace_name>
$ kubectl create namespace newspace
namespace/newspace created
kubectl command -n
$ kubectl get pod -n newspace
No resources found in newspace namespace.
kubectl delete namespace <namespace_name>
$ kubectl delete namespace newspace
namespace "newspace" deleted
newspace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: newspace
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: newspace-quotas-1
namespace: newspace
spec:
hard:
requests.cpu: "1"
limits.cpu: "1"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: newspace-quotas-2
namespace: newspace
spec:
hard:
services: "3"
secrets: "3"
configmaps: "3"
replicationcontrollers: "10"
Here is an example set of resources users may want to put under object count quota:
count/persistentvolumeclaims
count/services
count/secrets
count/configmaps
count/replicationcontrollers
count/deployments.apps
count/replicasets.apps
count/statefulsets.apps
count/jobs.batch
count/cronjobs.batch
count/deployments.extensions
若想知道更多關於resource quotas的話,請參閱https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/resource-quotas/
說完namespace後,我們就來談論Kubernetes去如何做到權限劃分的。
Kubernetes在1.8之後正式引入rbac,rbac全名為Role-Base Access Control 基於角色的訪問控制,它也是種管制訪問Kubernetes API的機制,管理員可以透過rbac.authorization.k8s.io 對授權進行動態的調配與設定。
也就是說Kubernetes的所有資源對象都是模組化後的API對象,允許執行CRUD,也就是以下資源:
...等
而Rbac就是去限制使用者對於這些物件訪問的授權調配。
那接下來就要介紹Rbac的幾位小老弟 Role, ClusterRole, RoleBinding, ClusterRoleBinding與serviceAccount
在rbac當中,我們透過ClusterRoleBinding、RoleBinding去綁定不同的ClusterRole、Role與ServiceAccount去限制每個Account所能在指定namespace下對物件進行的操作。
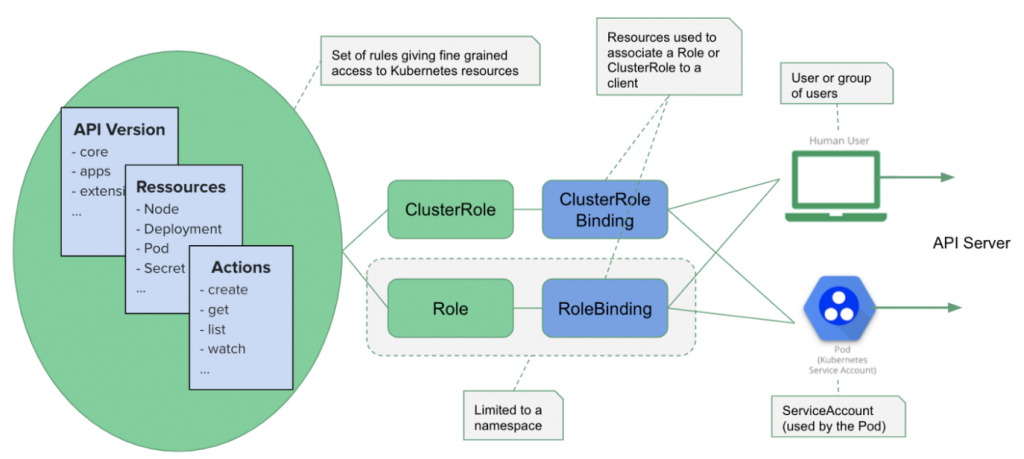
Role是用來定義在某個namespace下的角色,對於該namespace下物件的操作權限,我們直接以yaml來解說。
role.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: newspace
name: jenkins-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
我們這邊的Role他的權限只能
那麼再來我們將在role.yaml添加上serviceAccount,service Account是個讓外部訪問者使用的帳號,主要讓來讓像是CICD工具等進行訪問時設定的帳號,此外service account將會binding role來限制他的訪問權限。
role.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: newspace
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: newspace
name: jenkins-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
這邊我們建立一個名為jenkins的service account
如其名描述,就是用來binding role的物件,那我們一樣將RoleBinding加入role.yaml其中。
role.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: newspace
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: newspace
name: jenkins-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: jenkins-rolebinding
namespace: newspace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: jenkins-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: jenkins
namespace: newspace
$ kubectl apply -f role.yaml
serviceaccount/jenkins created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-role created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-rolebinding created
$ kubectl get rolebinding -n newspace
NAME ROLE AGE
jenkins-rolebinding Role/jenkins-role 26s
ClusterRole與Role相似,但他是屬於叢集通用角色的,也就是在該叢集內所有的namespace都通用該權限。也因此,它能比Role多配置
OK, 那我們來寫ClusterRole的yaml吧
clusterrole.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins-global
namespace: newspace
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: newspace
name: jenkins-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
這邊就不在贅述,他與Role相似,只是cluster role可以比role更多一些凌駕於namespace之上的資源進行權限配置。
人如其名,就是用來binding ClusterRole的object,那我們也將它加進clusterrole.yaml吧
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins-global
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
namespace: newspace
name: jenkins-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update","watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: jenkins-rolebinding
namespace: newspace
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: jenkins-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: jenkins-global
namespace: newspace
那這邊我們就結束了role與clusterrole的基本介紹。
本篇章所有程式碼將放在下面的github project當中的branch day-28
這篇章讓我們了解Kubernetes cluster在抽象層面是如何有效地區分不同使用者對於不同物件的權限設定,這在往後我們使用些CICD工具進行持續性交付與自動化佈署時,不會讓這些工具擁有太多的權限,產生安全性上的疑慮。
https://www.weave.works/blog/optimizing-cluster-resources-for-kubernetes-team-development
https://medium.com/better-programming/k8s-tips-using-a-serviceaccount-801c433d0023
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/
