本文同步更新於個人網站中,有更好的排版和程式碼區塊 highlighting 支援。
我們昨天已經看過了單向及雙向的鏈結串列,今天我們再來看看另外兩種鏈結串列。
有序鏈結串列跟前面兩種鏈結串列相比,就是在插入節點時,保證資料是有序的。陣列在向中間插入、移除資料時,其中一側的資料都要往後或向前移動,但鏈結串列就不需要煩惱這個。
有序鏈結串列的許多功能與單向鏈結串列和雙向鏈結串列相同,沒有必要再寫一次,直接用繼承的方式就可以了,然後在原類別的基礎上新增 3 個方法:find、insert、value。其中 find 方法需要一點技巧,因為插入時,我們只能插入到比目標值大的節點前面,不能使用等於,而在移除時,我們又想準確刪除 data 等於 value 的節點,因此設置了第 2 個參數 useByInsert 進行區分。但為了防止使用者誤傳一個參數,我們可以傳入一個唯一的 flag 進行比較。
實作程式碼如下:
const useByInsert = Symbol('useByInsert');
class SortedList extends DoublyList {
find(value, second) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
while (current) {
if (second === useByInsert ? current.data > value : current.data === value) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
i++;
}
}
insert(value) {
let next = this.find(value, useByInsert);
let node = new DoublyNode(value);
if (!next) {
let last = this.tail;
// 如果沒有節點比它大,它就是 tail
this.tail = node;
if (last) {
// append
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
} else {
// 什麼也沒有,它就是 head
this.head = node;
}
} else {
let prev = next.prev;
if (!prev) {
this.head = node;
this.head.next = next;
} else {
prev.next = node;
node.prev = prev;
}
node.next = next;
next.prev = node;
}
this.length++;
}
remove(value) {
let node = this.find(value);
if (node) {
let prev = node.prev;
let next = node.next;
if (!prev) {
this.head = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
}
if (next) {
next.prev = prev;
} else {
this.tail = prev;
}
this.length--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
const list = new SortedList();
list.insert(222);
list.insert(111);
list.insert(333);
list.insert(555);
list.insert(444);
list.insert(777);
list.insert(666);
console.log(list);
我們在 main.js 實際執行上面的程式碼後可以在控制台看到如圖的輸出:
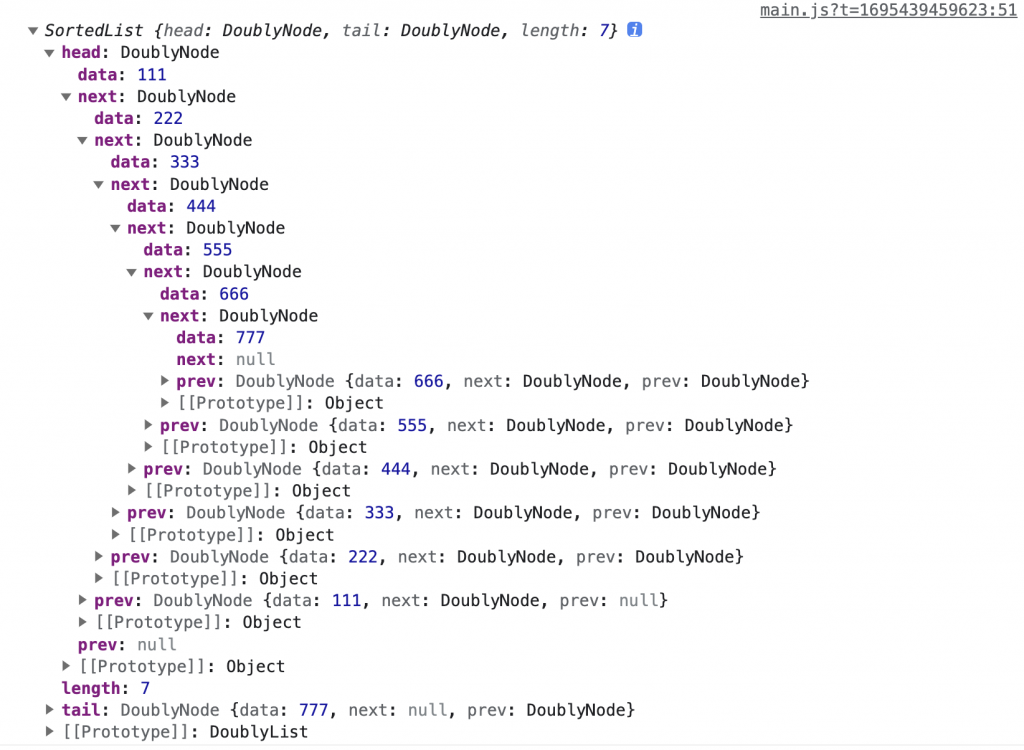
可以觀察到節點都是按照 data 的大小排列的。
有一道非常有名的面試題:約瑟夫問題(Josephus problem),會使用到環狀鏈結串列。
先了解一下規則:在一個房間裡有 n 個人(編號 0 ~ n-1),只能有最後一個人活下來。按照如下的規則進行:
所描述的規則可以用下圖的約瑟夫環來表示:
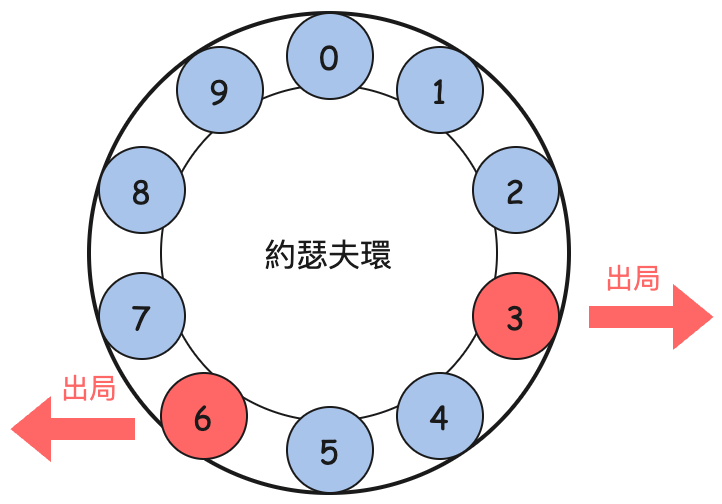
接下來你要做的就是:當你在這一群人之間時,你必須選擇一個位置讓你成為剩餘的最後一人。
這看起來很困難,但是有了環狀鏈結串列,就很好解決了。首先在雙向鏈結串列的 head 與 tail 是不同的節點,而環狀鏈結串列的這兩個都指向同一處。既然如此我們只保持一個 head 就足夠了。其次,forEach 與 find 方法需要做一下處理避免無限迴圈。因為只有一個節點的環狀鏈結串列,它的 next 和 prev 都會指向自己。
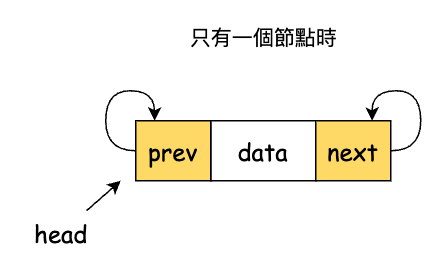
來看一下雙向鏈結串列和環狀鏈結串列的 forEach 方法:
// 雙向鏈結串列
forEach(cb) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
while (current) {
cb(current.data, i);
current = current.next;
i++;
}
}
// 環狀鏈結串列
forEach(cb) {
let current = this.head;
let first = this.head;
let i = 0;
while (current) {
cb(current.data, i);
current = current.next;
if (current === first) {
break; // 迴圈結束
}
i++;
}
}
我們模仿實作有序鏈結串列的時候,讓它繼承雙向鏈結串列,然後重寫 forEach、findIndex、insertAt 與 removeAt 方法:
class CircularLink extends DoublyList {
forEach(cb) {
let current = this.head;
let first = current;
let i = 0;
while (current) {
cb(current.data, i);
current = current.next;
if (current === first) {
break;
}
i++;
}
}
findIndex(index) {
const n = this.length;
if (index > n) {
return null;
}
// 判斷尋找方向
const dir = index > Math.floor(n / 2);
let current = dir ? this.head.prev : this.head;
let first = current;
let prop = dir ? 'prev' : 'next';
let add = dir ? -1 : 1;
let i = dir ? n - 1 : 0;
while (current) {
if (index === i) {
return current;
}
current = current[prop];
if (current === first) {
return current;
}
i += add;
}
return null;
}
insertAt(index, data) {
if (index <= this.length) {
const node = new DoublyNode(data);
if (index === 0 && !this.head) {
this.head = node;
node.prev = node;
node.next = node;
} else {
let prev = this.findIndex(index - 1);
let next = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
node.prev = prev;
node.next = next;
next.prev = node;
}
this.length++;
}
}
removeAt(index) {
const node = this.findIndex(index);
if (node) {
if (node.next === node) {
this.head = null;
} else {
let prev = node.prev;
let next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
if (node === this.head) {
this.head = next;
}
}
this.length--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
const list = new CircularLink();
list.insertAt(0, 111);
list.insertAt(1, 222);
list.insertAt(2, 333);
list.insertAt(1, 444);
list.insertAt(3, 666);
list.forEach((el, i) => console.log(el, i));
list.removeAt(0);
console.log(list);
我們在 main.js 實際執行上面的程式碼後可以在控制台看到如圖的輸出:
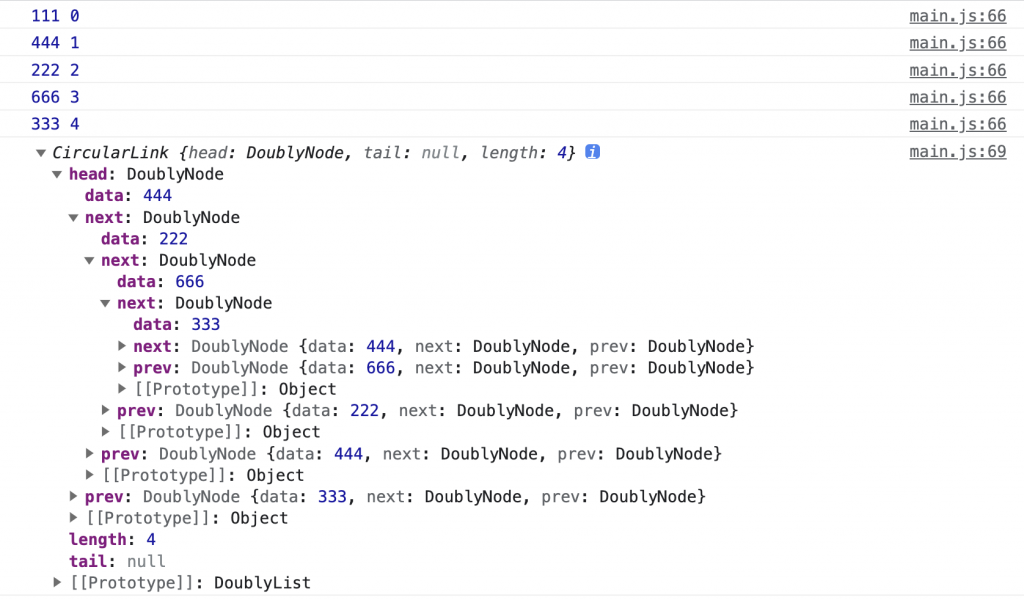
現在讓我們來解決約瑟夫問題,這個問題主要思路來自 forEach 與 remove 方法。我們先建立一個環狀的 list 與一個不斷遞迴呼叫的 kill 方法,kill 在只剩一個人時停止,如何判定只剩一個人,可以用 node.next === node 或 list.length === 1 來判斷。
function kill(list, node, m) {
let i = 1;
while (i <= m) {
if (i === m) {
if (node.next === node) {
console.log('最後一個', node.data);
return true;
}
let prev = node.prev;
let next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
list.length--;
if (node === list.head) {
list.head = next;
}
console.log('出局', node.data);
}
i++;
node = node.next;
}
kill(list, node, m);
}
function josephus(n, m) {
const list = new CircularLink();
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list.insertAt(i, i + 1);
}
kill(list, list.head, m);
return list.head.data;
}
其實這道題跟前面在講 queue 的時候提到的 Hot Potato 問題幾乎一樣,只是這次我們換成使用環狀鏈結串列來解決。
鏈結串列在建立的過程和陣列不同,陣列是連續的記憶體空間,而鏈結串列是零散的,每個節點都有自己的記憶體空間,並且每個節點都有指向下一個節點的指標,這樣就可以串起來了。當有資料要進來時,我們只需要根據指標找到下一個儲存空間的位置,然後把資料保存起來,接著指向下一個儲存資料的位置,這樣一來就可以把一些零散的記憶體空間利用起來了,雖然串列是線性表,但不會按照線性的順序儲存資料。
也因為鏈結串列是以這種方式儲存資料,所以它在插入和刪除資料時比較容易,只需要改變指標的指向就可以了,舉個例子: 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4,如果要在 1 和 2 之間插入一個 5,只需要把 5 的指標指向 2,然後把 1 的指標指向 5,這樣就完成了插入操作,不需要去管 5 實際的記憶體位置在哪裡,也不會對其他節點造成影響。但是如果是想要從串列中讀取一條資料,就要從 0 號開始一個一個往下找,直到找到我們要找的資料為止。
所以我們可以根據實際的需求來選擇使用陣列或鏈結串列,如果需要頻繁的插入和刪除操作,就可以使用鏈結串列,如果需要頻繁的查詢操作,就可以使用陣列。
