本文同步更新於個人網站中,有更好的排版和程式碼區塊 highlighting 支援。
我們都知道透過陣列索引的方式來查詢資料的效率非常高,而如果是鏈結串列的話,就需要透過線性搜尋的方式來查詢。可能有人會想,那麼我把所有的資料都存在陣列裡面不就好了嗎?
假設今天我們有十個數字(11, 2, 23, 35, 77, 94, 48, 56, 89, 100)要進行存放,按照剛才的思路,我們直接將它們自己當作索引存進陣列中會發生什麼事呢?我們會需要一個長度為 101 的陣列,然後再對應的索引上放上這十個數字,但是這麼做顯然有問題,因為出現了很多記憶體的浪費。
現在讓我們來做一點處理,我們將這十個數字 mod 10,得到的結果如下:
11 % 10 = 1
2 % 10 = 2
23 % 10 = 3
35 % 10 = 5
77 % 10 = 7
94 % 10 = 4
48 % 10 = 8
56 % 10 = 6
89 % 10 = 9
100 % 10 = 0
然後我們將取餘數後的結果作為索引,將這十個數字放進陣列中,這樣我們只需要一個長度為 10 的陣列就可以存取這十個數字了,假設將來我們要找 77 這個數字,我們只需要將 77 mod 10 得到 7,然後直接取陣列索引為 7 的元素就可以了,這就是雜湊表的基本思想。
我們已經知道,只要知道陣列的索引值就能快速定位到與之對應的元素,但如果索引值不是數字,而是一個字串,那麼該怎麼辦呢?如果我們能設法將一個字串通過某種算法轉換成一個數字,並且這個數字位於某個可接受的範圍(目的是讓底層的陣列不會過長,比如我們要新增 80 個數,那麼轉換成的索引值就不能大於 80),不就可以了嗎?對於增刪的問題,我們可以在元素位置上放入一個 linked list,這樣就能利用其操作很快的優點了。綜合以上優點的這個結合體就是雜湊表,一種透過雜湊演算法定位元素的線性結構。
其結構如下圖所示:
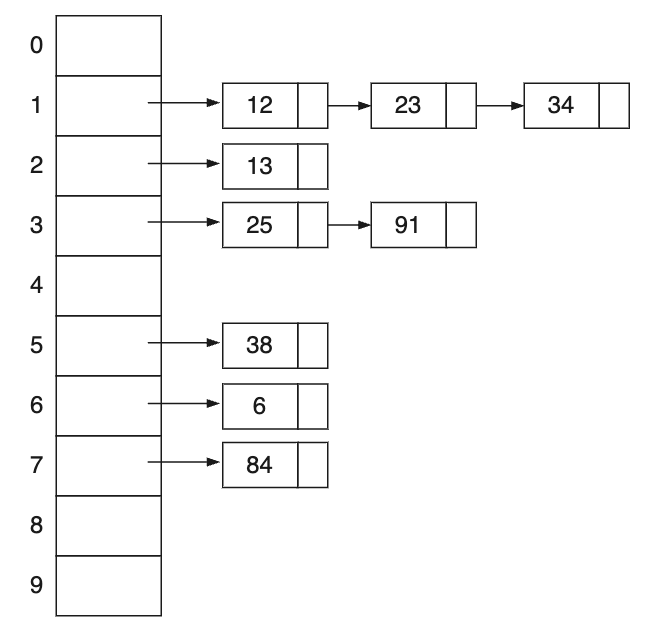
雜湊函式又叫作雜湊演算法,是一種將任意長度的訊息轉換成固定長度的雜湊值的函式,它可以把訊息或資料壓縮成摘要,使得資料量變小。這個函式會將資料打亂混合成一個雜湊值,這個值我們通常希望它是唯一的,然後我們利用這個值來定位元素,也就成了今天要介紹的雜湊表(Hash Table 或 Hash Map)。
雜湊函式的做法有很多種,我在最開始舉的例子中將數字 mod 10 其實就是一種雜湊函式,然而我們可以發現到,如果今天又多一個數字 22,那麼經過 mod 10 之後得到的索引值就會和 2 重複了,這就是所謂的碰撞(collision),然後今天又多了很多 2 結尾的數字,那麼這些數字就會都被放在索引值為 2 的位置上,這樣就會導致雜湊表的查詢效率下降,因為在 index 2 的位置上串了一堆資料,然後我們還需要透過線性搜尋的方式來找到我們要的資料,這樣就和我們一開始的目的背道而馳了。所以在這種情況下 mod 10 就不是一個好的雜湊函式。
通常會有幾種方法,然後我們會根據資料的形式或分佈來決定要選擇什麼方式去設計出合適的雜湊函式。
雜湊函式的選擇原則如下:
m,填入表中的節點數為 n,則稱比值 n/m 為雜湊表的 load factor(表示雜湊表中元素的填滿程度)。load factor 越大,填滿的元素越多,反之,則越少,其取值的範圍一般為 0.65 ~ 0.9。雜湊函式的建構方法有以下幾個:
先實作一個簡單不做碰撞處理的雜湊表:
class Hash {
constructor() {
this.table = new Array(1000);
}
hash(data) {
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
total += data.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 把字串轉成 Unicode 之後進行加總然後平方
const s = total * total + '';
// 保留中間 2 位
const index = s.charAt(s.length / 2 - 1) * 10 + s.charAt(s.length / 2) * 1;
console.log('hash value: ' + data + ' -> ' + index);
return index;
}
insert(key, data) {
const index = this.hash(key);
this.table[index] = {
name: key,
data: data,
};
}
get(key) {
const index = this.hash(key);
const node = this.table[index];
return node?.data;
}
forEach(cb) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
const node = this.table[i];
if (node) {
cb(node.data, node.name);
}
}
}
}
const someNames = [
'David',
'Jennifer',
'Donnie',
'Raymond',
'Cynthia',
'Mike',
'Clayton',
'Danny',
'Jonathan',
];
const hash = new Hash();
for (let i = 0; i < someNames.length; i++) {
hash.insert(someNames[i], someNames[i]);
}
hash.forEach((el, i) => {
console.log(el, i);
});
執行上面的程式碼可以得到以下結果:
hash value: David -> 81
hash value: Jennifer -> 74
hash value: Donnie -> 60
hash value: Raymond -> 29
hash value: Cynthia -> 84
hash value: Mike -> 21
hash value: Clayton -> 29
hash value: Danny -> 60
hash value: Jonathan -> 7
Jonathan Jonathan
Mike Mike
Clayton Clayton
Danny Danny
Jennifer Jennifer
David David
Cynthia Cynthia
在建立雜湊表時,存在一個問題:對於兩個不同的 key,透過 hash function 轉換後得到的雜湊值可能相同,這種情況稱為碰撞(collision)。如圖所示:
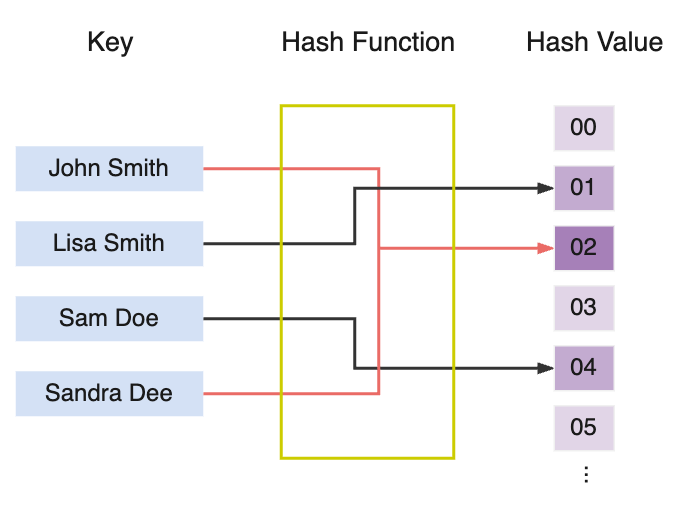
即使是經過上面提過的各種方法設計出好的雜湊函式,很多時候也很難避免完全不發生碰撞,甚至可能因為雜湊函式設計得過於複雜,反而會導致效率降低。所以一些小碰撞是可以接受的,那麼通常會怎麼去處理呢?
處理碰撞的技術可以分成兩類:開放雜湊(open hashing)和閉合雜湊(closed hashing)。開放雜湊方法是將碰撞記錄在表外,而閉合雜湊方法是將碰撞記錄在表內的另一個位置上。
open hashing 最著名的實現方法是鏈結法(chaining),它把雜湊中的每個槽(底層陣列的元素)定義為一個 linked list 的 head,雜湊到一個特定槽的所有記錄都放到這個槽的子鏈中。我們在新增元素時,先通過 hash function 計算出索引值,然後判斷是否為空,不為空則遍歷該 linked list 檢查是否已經保存相同的值。否則就建立一個新節點,將其插入到陣列中,原本的 list 則掛在新節點的 next 屬性。刪除時為了方便,就直接將 list 的 data 屬性重置為 null。
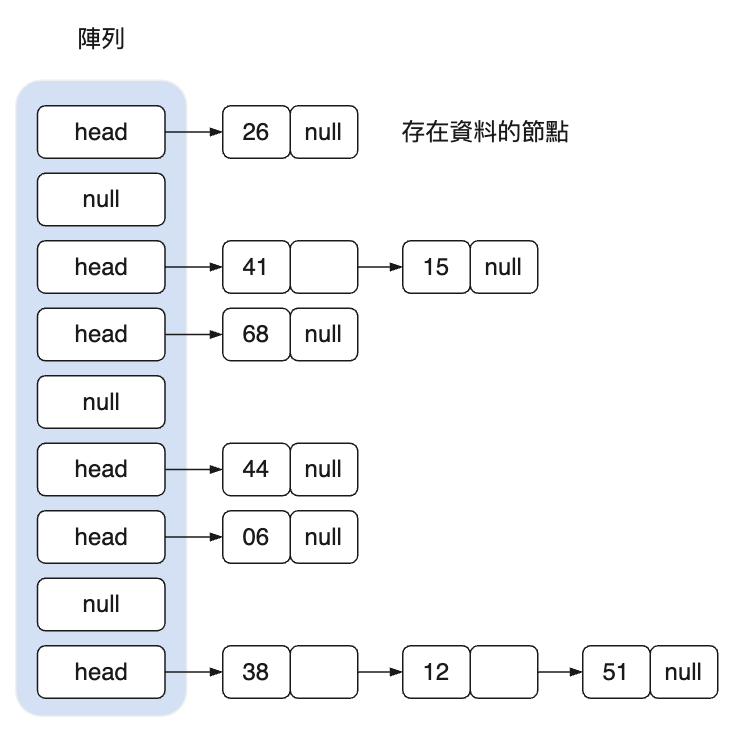
實作程式碼如下:
class Node {
constructor(name, data) {
this.name = name;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Hash {
constructor() {
this.table = [];
}
hash(key) {
key += ''; // 強制轉成字串
let HASHSIZE = 100;
let h = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
h = key.charCodeAt(i) + h * 31;
}
// 將整個字串按照特定關係轉化成一個整數,然後對雜湊長度取餘數
return h % HASHSIZE;
}
loopup(key) {
const hashvalue = this.hash(key);
let node = this.table[hashvalue];
while (node) {
if (node.name == key + '') {
return node;
}
node = node.next;
}
}
get(key) {
const node = this.loopup(key);
return node ? node.data : null;
}
remove(key) {
const node = this.loopup(key);
if (node) {
node.data = null;
}
}
insert(key, data) {
const hashvalue = this.hash(key);
// 不管這個雜湊位置有沒有其他節點,直接插入節點
let node = this.table[hashvalue];
let next = node;
if (node) {
while (node) {
if (node.name === key + '') {
node.data = data;
return; // key data 一致
}
node = node.next;
}
}
let np = new Node(key, data);
this.table[hashvalue] = np;
np.next = next;
}
forEach(cb) {
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) { // HASHSIZE = 100
if (this.table[i]) {
let link = this.table[i];
while (link) {
if (link.data !== null) {
cb(link.name, link.data);
}
link = link.next;
}
}
}
}
}
closed hashing 可選擇的方案有很多,閉合雜湊將所有記錄都直接存在雜湊表中,可以想成有人佔了你的位置(碰撞發生),你就按照某種規則再去佔別人的位置。這樣做的好處是使用的空間較固定,但如果碰撞嚴重時效率不佳。
線性探測與平方探測的對比圖如下:
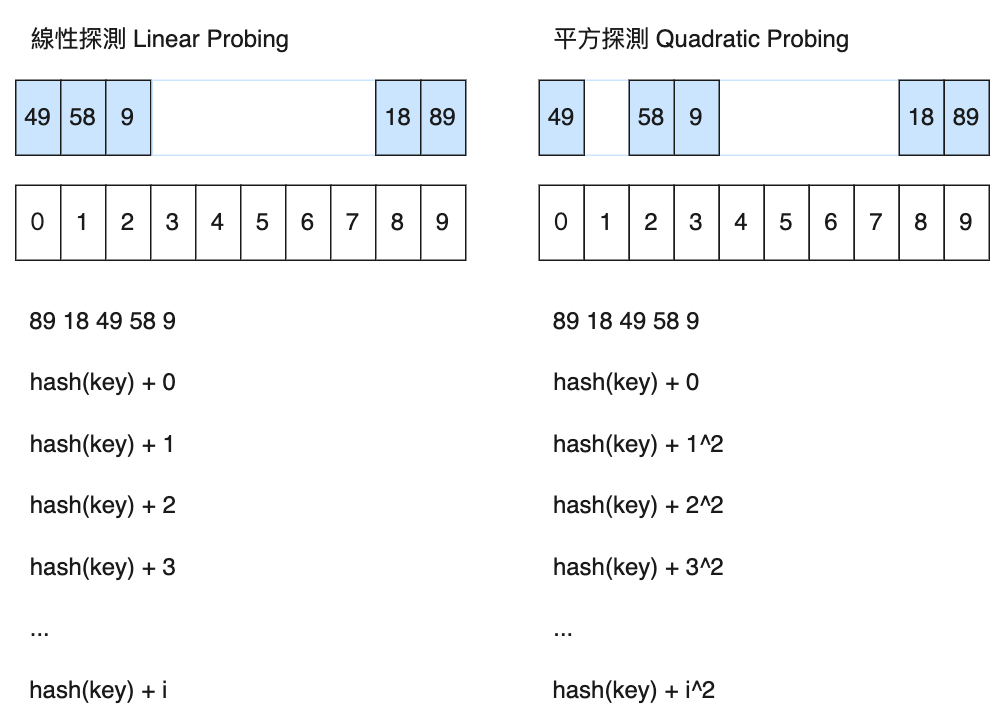
從使用效果來看,線性探測不如平方探測,因為線性探測最後會導致索引值都聚集在一起,當資料量大了之後,探測的次數會越來越多。
下面是使用平方探測的實作程式碼:
class Node {
constructor(name, data) {
this.name = name;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.state = true;
}
}
class Hash {
constructor() {
this.table = [];
this.capacity = 100; // 容量
this.length = 0;
}
hash(s) {
let seed = 131;
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
hash = s.charCodeAt(i) + hash * seed;
}
return hash & 0x7fffffff;
}
getHash(key, capacity) {
return this.hash(key + '') % capacity;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
insert(key, value) {
let inserted = false;
const index = this.find(key, (item) => {
item.data = value;
if (!item.state) {
this.length++;
}
inserted = item.state = true;
});
if (!inserted) {
this.table[index] = new Node(key, value);
this.length++;
}
if ((this.length * 10) / this.capacity > 6) {
this.capacity *= 2;
}
return true;
}
find(key, cb) {
const table = this.table;
let index = this.getHash(key, this.capacity);
let i = 1;
while (table[index]) {
if (table[index].name === key + '') {
cb.call(this, table[index]);
}
index = index + 2 * i - 1;
index %= this.capacity;
i++;
}
return index;
}
get(key) {
let value = null;
this.find(key, (item) => {
if (item.state) {
value = item.data;
}
});
return value;
}
remove(key) {
let oldSize = this.length;
this.find(key, (item) => {
item.state = false;
this.length--;
if ((this.length * 10) / this.capacity < 6) {
this.capacity /= 2;
}
});
return this.length !== oldSize;
}
forEach(cb) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.capacity; i++) {
const el = this.table[i];
if (el && el.state) {
cb(el.name, el.data);
}
}
}
}
雜湊的應用非常廣泛,例如:資料壓縮、驗證資料的完整性、加密或是區塊鏈等等。如果關注在解題上的話最常見的應用就是 Hash Table,但我們通常不會去使用 Hash 這個類別,而是會直接使用空物件,JavaScript 的物件就是一種效能非常好的 Hash Table。
如果陣列都是字串或是數字,我們可以將其全部作為 Hash 索引的 key 放進去,利用 Hash key 的唯一性來去除重複元素。實作程式碼如下:
function removeDuplicates(arr) {
const hash = {};
arr.forEach((el) => {
hash['.' + el] = el; // 前面加個 "." 是為了保證順序
});
return Object.keys(hash).map((key) => hash[key]);
}
與上面那題差不多,不過每次放元素時會記錄次數,最後再遍歷一次找出次數為 1 的元素即可。實作程式碼如下:
function findNonRepeatingNumbers(arr) {
const hash = {};
arr.forEach((el) => {
if (hash[el]) {
hash[el].count++;
} else {
hash[el] = {
count: 1,
data: el,
};
}
});
const result = [];
Object.keys(hash).forEach((key) => {
if (hash[key].count === 1) {
result.push(hash[key].data);
}
});
return result;
}
twoSum 是一道經典題,網路上甚至有「不知兩數和,刷盡力扣也枉然」的小段子。
給定一個整數陣列和一個目標值(target),找出兩個數的和等於目標值,並回傳這兩個數的索引值。這題可以用暴力法,但是時間複雜度會是 ,我們可以利用 Hash Table 來實作,一邊尋找一邊記錄,這樣時間複雜度就會降到
。實作程式碼如下:
function twoSum(numbers, target) {
const hash = new Hash();
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
const el = numbers[i] + '';
if (hash.get(el) !== null) {
const index = hash.get(el);
return [index, i];
}
hash.insert(target - el + '', i); // 在我們的實作中 key 要是字串
}
}
// 或是直接使用內建的 Map,因為 Map 的 key 具有唯一性
function twoSum(numbers, target) {
const hash = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
const el = numbers[i];
if (hash.has(target - el)) {
return [hash.get(target - el), i];
}
hash.set(el, i);
}
}
