這篇來看 Cluster Role & Cluster Role Binding,以及 Account 後綁定的作用對象。
類似於 Role,Cluster Role 也是用來定義這個角色可以做什麼的 Object。但 Cluster Role 顧名思義是作用於 Cluster Level。如果這個角色要操作的對象是沒有 Namespace 概念的,例如 nodes、namespaces、persistentvolumes、storageclasses etc,則使用 Cluster Role 來定義這個角色可以對資源做什麼操作。
用下面的指令可以確認哪些資源是 Namespaced、哪些不是
kubectl api-resources --namespaced=false
kubectl api-resources --namespaced=true
Cluster Role example manifest -
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: view-nodes
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
不過 Cluster Role 所套用的 rules 也可以是 Namespace level objects,這時這個角色就可以對 所有 Namspace 中的該資源做操作。
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-pod-operator
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "create", "update", "delete"]
像這個 Cluster Role 就可以對所有 Namespace 中的 Pods 做操作。
接下來要將 Account 與 Cluster Role 綁定,會需要使用 Cluster Role Binding 這個 Object。
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: view-nodes-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: viewer
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: view-nodes
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Cluster Role Binding 的 spec 寫法與 Role Binding 幾乎相同,一樣在 subjects 中指定要讓哪些 Service Accounts / User / Group 跟這個 Cluster Role 綁定。roleRef 指定是哪個 Cluster Role。
實際跑看看
執行以下的 yaml -
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sa-day23
namespace: test
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod
namespace: test
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
serviceAccountName: sa-day23
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cr1
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "create", "update", "delete"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: crb1
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sa-day23
apiGroup: ""
namespace: test
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cr1
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
進到 test namespace 中的 pod ,確認是否能 Access API server
# Point to the internal API server hostname
APISERVER=https://kubernetes.default.svc
# Path to ServiceAccount token
SERVICEACCOUNT=/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
# Read the ServiceAccount bearer token
TOKEN=$(cat ${SERVICEACCOUNT}/token)
# Reference the internal certificate authority (CA)
CACERT=${SERVICEACCOUNT}/ca.crt
# Explore the API with TOKEN
curl --cacert ${CACERT} --header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" -X GET ${APISERVER}/api
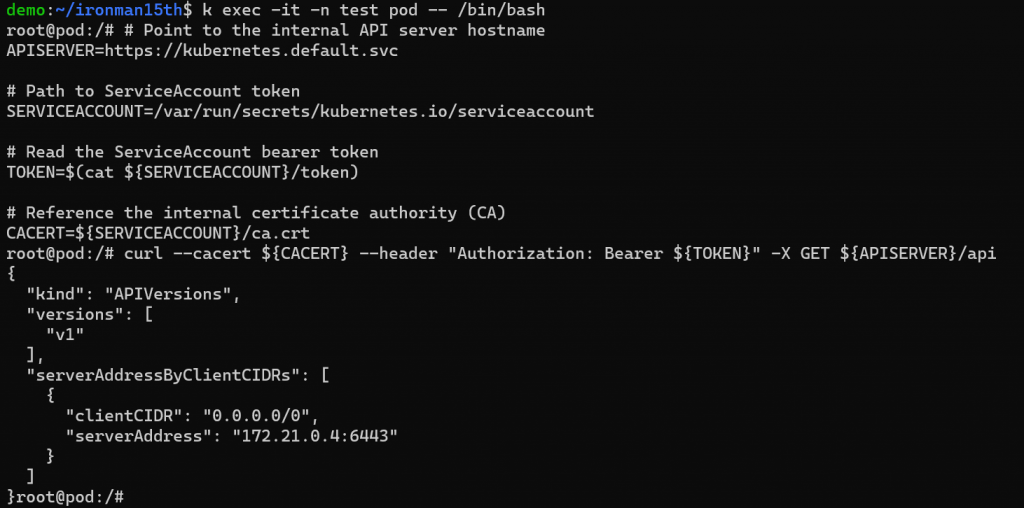
接下來測試是否能得到目前 Cluster 中 nodes 的資訊
curl --cacert ${CACERT} --header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" -X GET ${APISERVER}/api/v1/nodes
curl --cacert ${CACERT} --header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" -X GET ${APISERVER}/api/v1/nodes | jq '.items[] | .metadata.name'
因為 nodes 資訊太多,我另外在 pod 中安裝 jq 來抓 json 特定的 keyword。
apt update -y
apt install jq -y
Get Nodes 成功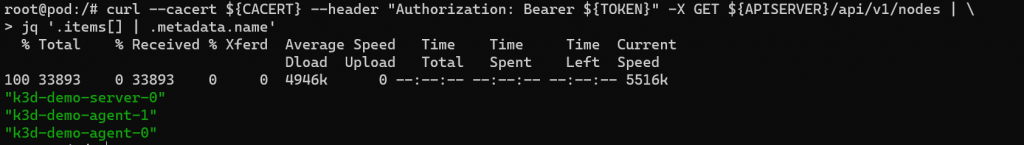
接下來對 Cluster 中的 Pods 做操作,列出所有 namespace 中的 pods
curl --cacert ${CACERT} --header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" -X GET ${APISERVER}/api/v1/pods
curl --cacert ${CACERT} --header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" -X GET ${APISERVER}/api/v1/pods | jq '.items[] | .metadata.name'
為了 demo 方便,一樣透過 jq 擷取 json 部分 key,可以看到這個 service account 能看到所有 namespace 的 pods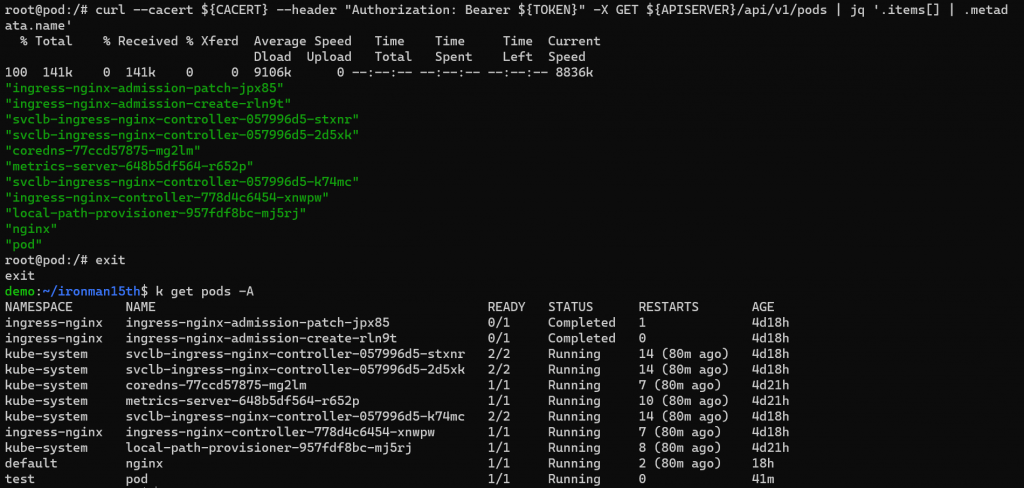
假設有兩個 Roles 都是對 Pod 做操作,一個是可以讀取 pods,一個是可以建立刪除編輯 pods。如果將同一個 Service Account 綁上兩個 Roles,權限會是疊加的。
執行以下 yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: multi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: multi-sa
namespace: multi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
namespace: multi
name: multi-pod
spec:
serviceAccount: multi-sa
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
# role1
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: multi
name: role-read
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
---
# role2
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: multi
name: role-edit
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "patch"]
---
# rolebinding1
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: multi
name: multi-rolebinding-read
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: multi-sa
namespace: multi
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-read
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
# rolebinding2
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: multi
name: multi-rolebinding-edit
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: multi-sa
namespace: multi
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-edit
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
以上的 yaml 做了以下的事情:
建立好後一樣可以進去 Pod 中,帶上 token 向 kube API server 發請求。不過這邊用另一個方式來檢查這個 Service Account 有沒有做什麼事的權限。可以利用 kubectl auth can-i 加上 <要執行的指令> 加上 --as flag,模擬這個 subject 能不能做什麼事。
# check if "multi-sa" service account in the multi namespace can get pods in "multi" namespace
kubectl auth can-i get pod -n multi --as system:serviceaccount:multi:multi-sa
# check if dev-user can create deployments in "test" namespace
kubectl auth can-i create deployments -n test --as dev-user
# check if myself can delete pods in default namespace
kubectl auth can-i delete pods -n default
可以觀察到我們建立的 multi-sa Service Account,可以讀取 Pods、也能刪除 Pods;不能執行的操作會回覆 no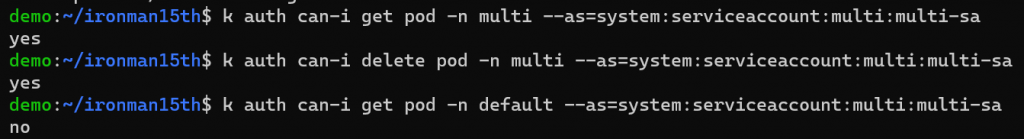
P.S.
API server 回傳的 Json 檔在 Terminal 上實在太難看懂,如果想要看 API server 回傳的 Json 內容,透過 kubectl proxy 能讓 Host 開瀏覽器看看。
kubectl proxy --port=8001 &
Reference
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/65981089/is-it-possible-to-have-more-than-1-role-with-1-service-account-in-different-name
