
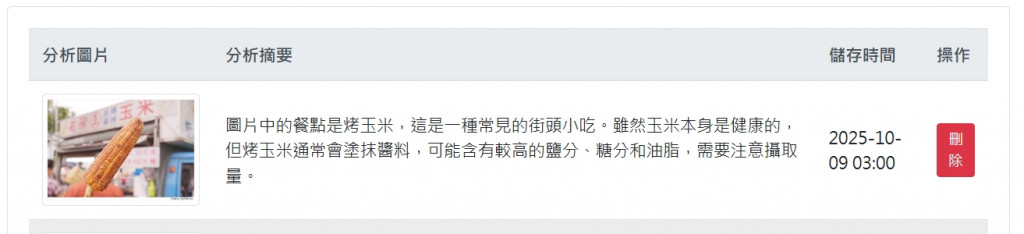
(圖片來源:由 Perplexity 協助生圖)
正如圖片所示,儲存飲食紀錄的目的之一,就是希望 AI 提供意見的時候,是根據自己的實際情況,而不是網路上漫無邊際的營養資訊,尤其是希望 AI 幫自己均衡一下飲食,給出具體的規劃時,更是如此
整個 RAG 流程的核心在於「索引」和「查詢」。當一筆新的飲食紀錄儲存時,系統會更新索引;當使用者提問時,系統會查詢索引,找到相關資料,最後交給 AI 生成答案。
main_controller.py)一切始於使用者儲存一筆飲食分析紀錄。
main_controller.py 中的 /save_record 路由。 # controllers/main_controller.py -> save_record()
# 儲存紀錄到資料庫
db.session.add(record)
db.session.commit()
# 將新儲存的紀錄加入 RAG 索引
try:
index_record(record)
except Exception as e:
print(f"RAG index failed: {e}")
rag_service.py 中的 index_record(record) 函式,將這筆新資料即時地加入到 RAG 的「知識庫」中。rag_service.py)倒排索引 (Inverted Index) - 關鍵字檢索
INVERTED_INDEX = defaultdict(set)
{'羊肉': {1, 5}, '蛋白質': {1, 8, 9}},表示ID為1和5的文件包含「羊肉」。index_record):
# in services/rag_service.py -> index_record()
def index_record(record):
doc_id = record.id
text = f"{record.summary or ''} {record.nutrients_json or ''}"
# 將文字切成字元
tokens = tokenize(text)
DOC_TOKENS[doc_id] = tokens
for t in tokens:
# 更新倒排索引
INVERTED_INDEX[t].add(doc_id)
向量索引 (Vector Index) - 語意檢索
DOC_EMBS = {}
index_record_vector):
# services/rag_service.py -> index_record_vector()
def index_record_vector(record):
text = f"{record.summary or ''} {record.nutrients_json or ''}"
# 呼叫 Gemini API 取得向量
emb = embeddings_service.get_embedding(text)
# 儲存向量
DOC_EMBS[record.id] = emb
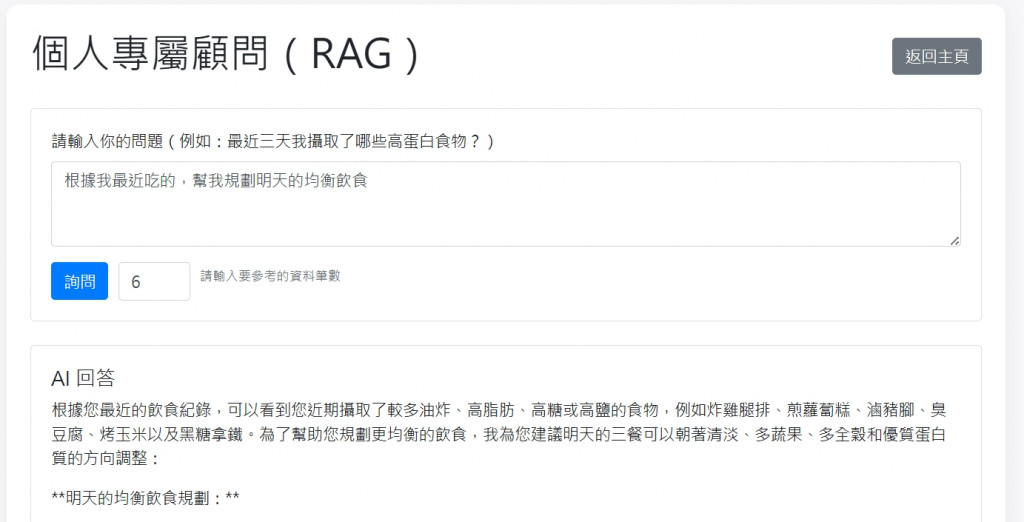
embeddings_service.py): 這個檔案負責呼叫 Google Gemini API,將文字轉為向量。main_controller.py & rag_service.py)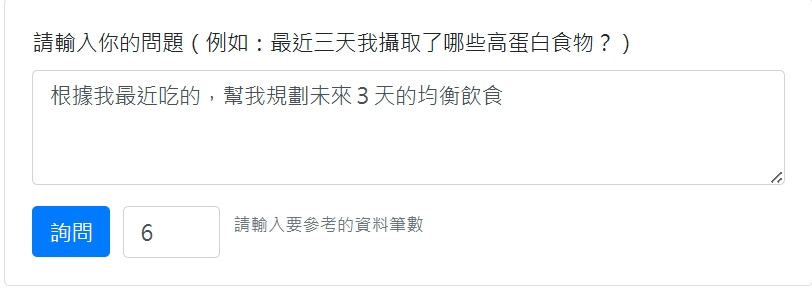

觸發點: main_controller.py 中的 /rag/query 路由。
程式碼:
# controllers/main_controller.py -> rag_query()
def rag_query():
question = data.get('question', '').strip()
# 1. 檢索 (Retrieval)
from services.rag_service import query_records
# 使用關鍵字檢索
search_results = query_records(question, top_k=top_k)
# 2. 增強 (Augmented):將檢索到的資料組合成上下文
context_text = "\n".join(contexts)
# 3. 生成 (Generation)
from services.gemini_service import generate_answer_from_context
# 交給 LLM
answer = generate_answer_from_context(question, context_text)
return jsonify({'answer': answer, 'sources': sources})
OpenAI 官方說明,介紹 GPT 如何透過檢索增強生成,並減少幻覺風險。
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Semantic Search for GPTs — OpenAI Help
維基百科條目,提供 RAG 的歷史背景、學術來源與技術變體。
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) — Wikipedia
聚焦於 RAG 的安全與合規議題,解釋如何在企業環境中安全部署 RAG 模型。
Nightfall AI Security 101: What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
