在 Day 13,我們討論了Chunking 策略,將 Notion 筆記切分成適合的文字片段,方便送進 Embedding 模型轉換成向量。
今天,我們要實作兩件事:
在 Day 11~Day 13,我們已經把 Notion 筆記寫進 SQLite (notion.db),並依照 ERD 拆成三張表:
其中,notion_blocks.block_text 是我們的主要目標,因為這些文字就是筆記的核心內容。
接下來,我們要將這些 block_text 撈出來,準備進行 Chunking。
src/fetch_notion_blocks.pyimport sqlite3
def fetch_blocks(db_path="data/notion.db", limit=1000):
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT block_id, page_id, block_text
FROM notion_blocks
WHERE block_text IS NOT NULL AND TRIM(block_text) <> ''
LIMIT ?
""", (limit,))
rows = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
return [{"block_id": r[0], "page_id": r[1], "text": r[2]} for r in rows]
if __name__ == "__main__":
blocks = fetch_blocks(limit=10)
for b in blocks:
print(b)
block_id, page_id, block_text。{
"block_id": "xxx",
"page_id": "yyy",
"text": "Block 文字內容"
}
fetch_blocks() 函式,可被其他模組呼叫(例如 chunk_text.py)。在 Day 13,我們已經介紹過 Chunking 的原則:
src/chunk_block_text.pyfrom fetch_notion_blocks import fetch_blocks
def chunk_text(text, chunk_size=800, overlap=100):
"""
將文字切成 chunks,避免超過 Embedding token 限制。
- chunk_size: 每段最大長度(字元數)
- overlap: 每段之間的重疊,避免語意斷裂
"""
chunks = []
start = 0
while start < len(text):
end = start + chunk_size
chunks.append(text[start:end])
start = end - overlap # 保留重疊
return chunks
def fetch_and_chunk(db_path="data/notion.db", limit=100):
"""
從 SQLite 撈出 blocks,再進行 chunking。
輸出格式:
[
{
"block_id": "...",
"page_id": "...",
"chunk_id": "block序號-第n段",
"text": "切割後的內容"
}
]
"""
blocks = fetch_blocks(db_path=db_path, limit=limit)
all_chunks = []
for b in blocks:
pieces = chunk_text(b["text"])
for idx, p in enumerate(pieces):
all_chunks.append({
"block_id": b["block_id"],
"page_id": b["page_id"],
"chunk_id": f"{b['block_id']}-{idx}",
"text": p
})
return all_chunks
if __name__ == "__main__":
chunks = fetch_and_chunk(limit=10)
for c in chunks:
print(c["chunk_id"], c["block_id"], c["text"][:80], "...")
chunk_size=800。overlap=100,相鄰 chunk 之間的重疊區,避免句子被硬切斷後失去語意連貫。fetch_blocks(),從 SQLite 撈出 notion_blocks 的文字。chunk_text() 進行切割。chunk_id:用 block_id-序號 來標示,方便追蹤。{
"block_id": "block123",
"page_id": "page123",
"chunk_id": "block123-0",
"text": "切割後的內容..."
}
text-embedding-3-smallOpenAI 在 2024 年初推出了 text-embedding-3 系列,主要有兩種規格:
text-embedding-3-small:維度 1,536,速度快、成本低,非常適合個人專案與知識檢索。text-embedding-3-large:維度 3,072,語意捕捉更細緻,適合需要極高準確度的大型應用(成本也較高)。我們選擇 text-embedding-3-small,理由如下:
text-embedding-3-small 的語意理解力,足以處理:
text-embedding-3-small 的支援。我們選擇了 OpenAI 目前性價比最高的 text-embedding-3-small 模型,它的定價是每百萬 tokens收費**$0.02**美元。
百萬 tokens 是什麼概念?大約是 75 萬個英文字,或 30-50 萬個中文字。聽起來很多,但實際費用呢?我們寫個小工具來算算看。
src/calc_embedding_cost.pyimport sqlite3
def fetch_block_lengths(db_path="data/notion.db", limit=1000):
"""撈出 block_text 並計算長度(粗估 token 用字數替代)。"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT block_text
FROM notion_blocks
WHERE block_text IS NOT NULL AND TRIM(block_text) <> ''
LIMIT ?
""", (limit,))
rows = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
return [len(r[0]) for r in rows if r[0]]
def calc_embedding_cost(num_chunks: int, avg_tokens_per_chunk: int, rate_per_million_tokens: float = 0.02):
"""估算 OpenAI Embedding API 的總成本。"""
total_tokens = num_chunks * avg_tokens_per_chunk
cost_usd = (total_tokens / 1_000_000) * rate_per_million_tokens
return total_tokens, cost_usd
if __name__ == "__main__":
lengths = fetch_block_lengths(limit=5000)
# 假設字數 ≈ token 數,這裡簡單用 1 char ≈ 1 token(保守估算)
total_tokens = sum(lengths)
avg_tokens_per_chunk = int(total_tokens / len(lengths)) if lengths else 0
total_tokens, cost_usd = calc_embedding_cost(len(lengths), avg_tokens_per_chunk)
cost_twd = cost_usd * 31 # 假設匯率 1 USD = 31 TWD
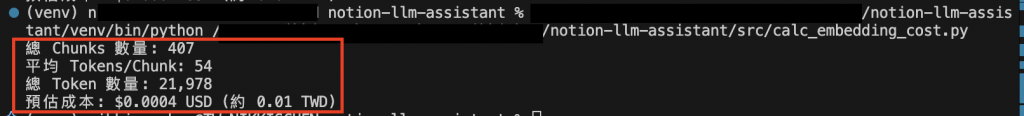
print(f"總 Chunks 數量: {len(lengths)}")
print(f"平均 Tokens/Chunk: {avg_tokens_per_chunk}")
print(f"總 Token 數量: {total_tokens:,}")
print(f"預估成本: ${cost_usd:.4f} USD (約 {cost_twd:.2f} TWD)")
今天我們完成了兩件事:
SQLite 撈出 Notion block 並進行 Chunking,讓文字能切成適合 Embedding 的片段。在 Day 15,我們將呼叫 Embedding API,把 chunks 轉成向量,進入語意檢索的世界!![]()
