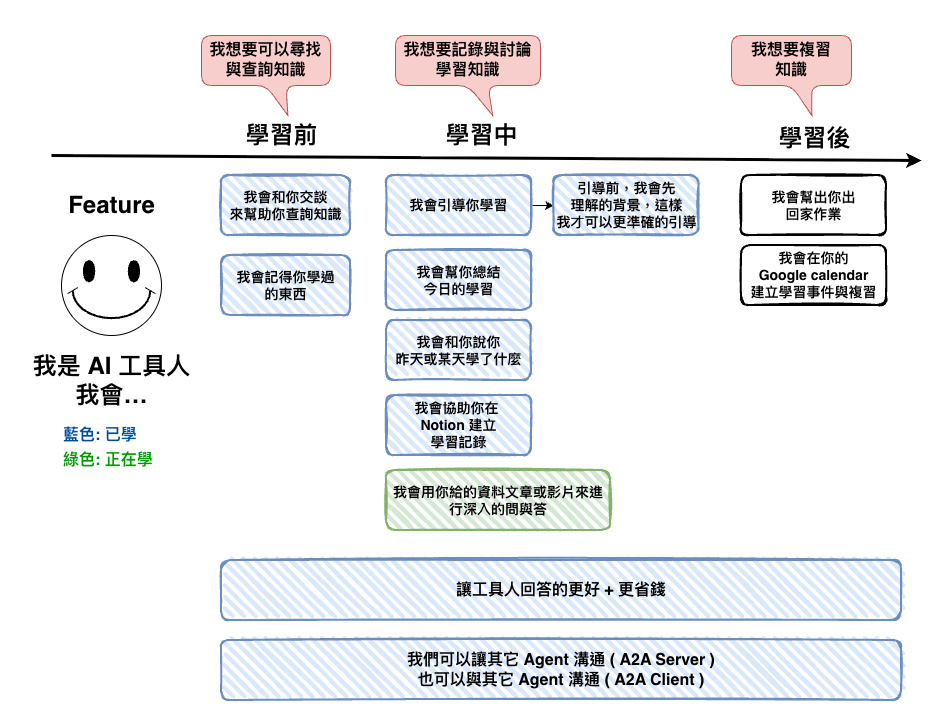
上一篇文章理解了 RAG 的基本概念後,接下來我們將以字幕檔實作 AI 課程問答這個題目,來深入理解整個 RAG 的流程與細節。
然後我們這篇文章主要先以最基本的Native RAG來進行實作。
我以陳縕儂教授的這部 Youtube 影片來當我們的範例,來實作 :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5_AXlDHHrmM&t=5s
和 AI 工具人討論這堂課程的內容
備註: 陳縕儂教授的很多部影片很棒棒,讓我學到不少東西。
然後接來的整個流程就是昨天的這張圖,然後我們這裡會以 MongoDB Atlas 來當我們的 Vector Database。
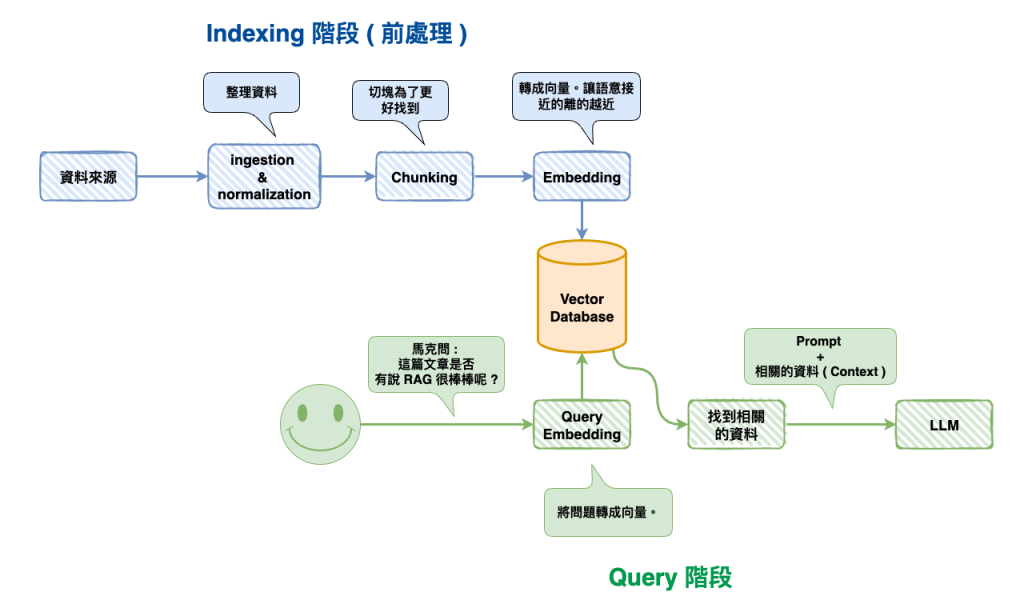
正常來說要對影片下手通常第一優先一定是字幕檔,不會用影片,因為太大了,麻煩又或錢。
首先這個是我們的字幕檔的部份資料,然後現網路上很多地方可以直接傳 youtube 就可以取得到他的字幕檔,然後通常就是 vtt、srt 等,然後我們這個是 srt 檔,大概長的如下。
1
00:00:00,000 --> 00:00:02,000
好,各位同學大家好
2
00:00:02,000 --> 00:00:04,000
我們今天呢
3
00:00:04,000 --> 00:00:06,000
要講的是
4
00:00:06,000 --> 00:00:08,000
RAG就是
5
00:00:08,000 --> 00:00:10,000
Retrieval Augmented Generation
我們這個部份主要有三段處理 :
🤔 1. 文字正規化( Normalization )
這裡就是要正規化文字,主要就是如下 :
🤔 2. 合併片段 ( Chunking )
這裡主要處理的是語意斷裂的問題,例如你看我們第 2、3 段的『 我們今天呢 』與『 要講的是 』這兩段,它是不是合在一起,我們反而比較知道它的語意呢 ?
1
00:00:00,000 --> 00:00:02,000
好,各位同學大家好
2
00:00:02,000 --> 00:00:04,000
我們今天呢
3
00:00:04,000 --> 00:00:06,000
要講的是
正常情況下,有以下兩種方法來處理這一塊 :
然後等一下你看 code 時會有以下的參數,他們的解釋如下。
然後白話文就是,如果字幕片段太短 (少於 3 秒或 8 字)、或跟下一句幾乎連在一起(間隔不到 1 秒),就合併起來變成一段完整的話,目標抓 8-12 秒,最多不超過 20 秒。
這個在不使用 AI 的情況下,應該還算是個可以堪用的處理手法,我從 AI 這學到的。
備註: Chunking 事實上還有下面這些策略選擇,但這裡就先以簡單的版本
🤔 3. 結構化成 Json 為了好擴展
這個可以有助於幫助我們進行後面的處理,並且也比較好儲放到資料庫中。
🤔 這一部份的整段程式碼
import fs from "fs";
interface SRTSegment {
index: number;
startMs: number;
endMs: number;
durationMs: number;
text: string;
}
interface ProcessedChunk {
chunkId: string;
startMs: number;
endMs: number;
durationMs: number;
textRaw: string;
textClean: string;
lang: string;
}
class SRTProcessor {
/**
* 解析時間碼轉毫秒
* "00:00:02,000" -> 2000
*/
private static parseTimestamp(timestamp: string): number {
const [time, ms] = timestamp.split(",");
const [hours, minutes, seconds] = time.split(":").map(Number);
return hours * 3600000 + minutes * 60000 + seconds * 1000 + Number(ms);
}
/**
* 文字正規化 - 統一轉半型
*/
private static normalizeText(text: string): string {
return (
text
// 只 replace 需要轉換的字元 (更高效)
.replace(/[!-~、 ]|[,。!?;:「」『』()【】《》]/g, (char) => {
const code = char.charCodeAt(0);
// 全型 ASCII (FF01-FF5E) 轉半型
if (code >= 0xff01 && code <= 0xff5e) {
return String.fromCharCode(code - 0xfee0);
}
// 有些字元不在 0xFF01-0xFF5E 範圍內! 需要手動轉換
const map: Record<string, string> = {
",": ",",
"。": ".",
"!": "!",
"?": "?",
";": ";",
":": ":",
"「": '"',
"」": '"',
"『": "'",
"』": "'",
"(": "(",
")": ")",
"【": "[",
"】": "]",
"《": "<",
"》": ">",
"、": ",",
" ": " ",
};
return map[char] || char;
})
.replace(/\s+/g, "")
.trim()
);
}
/**
* 備註: 這個可以不用有,但我想儲放一下
* 估算 token 數(粗略:中文字數 + 英文單詞數)
*/
private static estimateTokens(text: string): number {
const chineseChars = (text.match(/[\u4e00-\u9fa5]/g) || []).length;
const englishWords = (text.match(/[a-zA-Z]+/g) || []).length;
return chineseChars + englishWords;
}
/**
* 解析 SRT 文件
*/
static parseSRT(srtContent: string): SRTSegment[] {
const segments: SRTSegment[] = [];
const blocks = srtContent.trim().split(/\n\s*\n/);
for (const block of blocks) {
const lines = block.trim().split("\n");
if (lines.length < 3) continue;
const index = parseInt(lines[0]);
const [startStr, endStr] = lines[1].split(" --> ");
const text = lines.slice(2).join("\n");
const startMs = this.parseTimestamp(startStr);
const endMs = this.parseTimestamp(endStr);
segments.push({
index,
startMs,
endMs,
durationMs: endMs - startMs,
text
});
}
return segments;
}
/**
* 合併片段
*/
static mergeSegments(
segments: SRTSegment[],
options: {
minDuration?: number; // 最小片段時長 (ms)
minChars?: number; // 最小字數
maxGap?: number; // 最大間隔 (ms)
targetDuration?: number; // 目標時長 (ms)
maxDuration?: number; // 最大時長 (ms)
} = {}
): SRTSegment[] {
const {
minDuration = 3000,
minChars = 8,
maxGap = 700,
targetDuration = 8500,
maxDuration = 20000,
} = options;
const merged: SRTSegment[] = [];
let current: SRTSegment | null = null;
for (let i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) {
const segment = segments[i];
const nextSegment = segments[i + 1];
if (!current) {
current = { ...segment };
continue;
}
// 計算間隔
const gap = segment.startMs - current.endMs;
const currentChars = current.text.length;
const wouldBeDuration = segment.endMs - current.startMs;
// 判斷是否應該合併
const shouldMerge =
(current.durationMs < minDuration ||
currentChars < minChars ||
gap <= maxGap) &&
wouldBeDuration <= maxDuration;
if (shouldMerge) {
// 合併
current.text += "\n" + segment.text;
current.endMs = segment.endMs;
current.durationMs = current.endMs - current.startMs;
} else {
// 儲存當前,開始新的
merged.push(current);
current = { ...segment };
}
// 如果已達目標時長且不是最後一段,考慮結束合併
if (current.durationMs >= targetDuration && nextSegment) {
const nextGap = nextSegment.startMs - current.endMs;
if (nextGap > maxGap) {
merged.push(current);
current = null;
}
}
}
// 加入最後一段
if (current) {
merged.push(current);
}
return merged;
}
/**
* 清理合併後的文本
*/
private static cleanMergedText(text: string): string {
return text
.split("\n")
.map((line) => line.trim())
.filter((line) => line.length > 0)
.join("、")
.replace(/([^。!?])$/, "$1。"); // 句末補句號
}
/**
* 完整處理流程
*/
static process(
srtContent: string,
sectionPath?: string
): ProcessedChunk[] {
// 1. 解析 SRT
const segments = this.parseSRT(srtContent);
// 2. 合併
const merged = this.mergeSegments(segments);
// 3. 生成最終結果
return merged.map((segment, index) => {
const textRaw = segment.text;
const textClean = this.cleanMergedText(
this.normalizeText(textRaw)
);
return {
chunkId: `utt-${String(index + 1).padStart(4, "0")}`,
startMs: segment.startMs,
endMs: segment.endMs,
durationMs: segment.durationMs,
textRaw,
textClean,
lang: "zh"
};
});
}
}
const srtContent = fs.readFileSync("./test.srt", "utf-8");
const processedChunks = SRTProcessor.process(srtContent, "30-21");
console.log(processedChunks);
🤔 1. 建立 mongodb atlas vector search idnex
https://www.mongodb.com/zh-cn/docs/atlas/atlas-vector-search/vector-search-type/#how-to-index-fields-for-vector-search
這個地方我主要是去 atlas ui 直接建立,它也可以寫程式碼,然後主要填寫欄位如下,其中重點是以下兩個欄位 :
{
"fields": [
{
"type": "vector",
"path": "embedding",
"numDimensions": 1536,
"similarity": "cosine|dotProduct|euclidean"
}
]
}
🤔 2, 存進向量資料庫
我們這裡會使用 OpenAI 的 text-embedding-3-small 來當我們 embedding 模型,因為雖然不算是繁體中文最好,但應該是 CP 值比較平衡的。
然後這裡我們用 MongoDB Atlas 來當向量資料庫,主要的原因還是在於公司吧,我自已是還沒認真的和其它向量資料庫來比,但目前看起來評價與用起來還不錯,而且主要公司也有在用,所以才拿他來說說。
順到說一下,現在技術選型我事實上也蠻看重現有公司的技術體系,不太因為某個技術非常棒棒,就決定轉過去,因為還是要考慮維護與團隊的平衡,你自已想想每個資料庫都有自已的特色,如果真的用這個特色來決定用他,那會不會你做了 5 個需求,結果公司就用了 5 套資料庫呢 ? 大公司有專業的 SRE 就算了,小公司最後只會讓維護的人罵你髒話。
const client = new MongoClient(MONGODB_URI);
const collection = client.db(DATABASE_NAME).collection(COLLECTION_NAME);
const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({
modelName: "text-embedding-3-small",
});
const vectorStore = new MongoDBAtlasVectorSearch(embeddings, {
collection,
indexName: VECTOR_INDEX_NAME,
textKey: "text",
embeddingKey: "embedding",
});
const indexing = async () => {
const srtContent = fs.readFileSync("./test.srt", "utf-8");
const processedChunks = SRTProcessor.process(srtContent, "30-21");
for (const chunk of processedChunks) {
await vectorStore.addDocuments([
{
pageContent: item.text_clean,
metadata: item,
},
]);
}
};
好了以後應該會看到結果如下 :

我們以 hallucination 是什麼?來當情境來看看答案。
await query('hallucination 是什麼?');
const query = async (message: string) => {
const retriever = vectorStore.asRetriever({
k: 5,
});
const contexts = await retriever.invoke(message);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: "gpt-5-mini",
});
const result = await model.invoke([
{
role: "system",
content: `
# Context: ${contexts
.map((context) => {
return JSON.stringify({
content: context.pageContent,
startAt: context.metadata.start_ms,
endAt: context.metadata.end_ms,
});
})
.join("\n")}
# Additional & Limit:
- 你只能根據 Context 回答相關的問題,並且說明答案的來源時間範圍
- 時間範圍格式為 "MM:SS~MM:SS"
- 限制在 100 個字以內
`,
},
{ role: "user", content: message },
]);
console.log(result);
};
結果如下,然後我回去看了影片的位置的確是正確沒錯的。
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-CNJmptJk0FdVTepLu7mK9GMyFBUX2",
"content": "hallucination 是模型憑空編造或誇大事實的錯誤回答,例如虛構自己從 Stanford 畢業。來源:02:20~02:40",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"promptTokens": 550,
"completionTokens": 818,
"totalTokens": 1368
},
"finish_reason": "stop",
"model_name": "gpt-5-mini-2025-08-07"
},
"tool_calls": [],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"output_tokens": 818,
"input_tokens": 550,
"total_tokens": 1368,
"input_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"cache_read": 0
},
"output_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"reasoning": 768
}
}
}
這篇文章中我們實作了根據字幕來進行問與答的功能開發,但事實上最後的結果事實上有點主觀,我們也不能用這個一次的嘗試就說這個 RAG 很棒棒,之後會有篇文章來研究研究『 評估 』這一塊的東西。
然後接下來我們將要來研究Advanced RAG。
