近年來,深度偽造(DeepFake)已經造成假影片氾濫,從剛開始的美國總統Obama的談話影片,到最近明星臉全部被套到各式的影片當中,真偽難辨,它根源的技術就是【生成式對抗網路】(Generative Adversarial Network, GAN),相關的介紹可以參照【Day 28:小學生談『生成對抗網路』(Generative Adversarial Network,GAN)】一文,本篇不再贅述,將主題放在如何使用Keras實作GAN。
根據【GAN Zoo】統計,2014~2018年 GAN 各式的演算法就有 502 個,比較炫的演算法可以參閱【Some cool applications of GAN】,摘要部分如下:
動漫人物創作(Create Anime characters)。
各種姿勢生成(Pose Guided Person Image Generation):加上各種姿勢的關鍵點,GAN可以生成模特兒的各種站姿。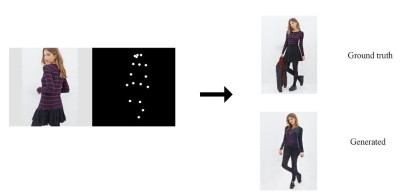
跨領域變換(Cross-domain transfer):類似風格轉換,但只換目標物,例如下圖,將一般的馬加上斑馬紋,也能作相反的變換。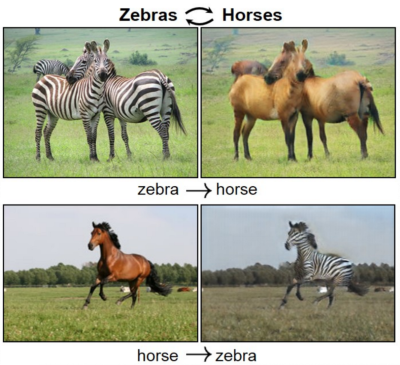
提升解析度(Super resolution)。
換臉(Progressive growing of GANs)
由影像分割(image segmentation)產生真實影像,右半圖變換為左半圖。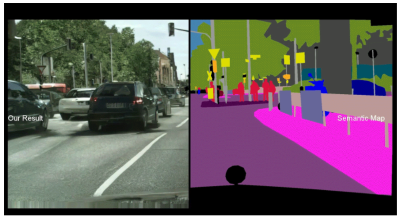
類似生成影像的應用,不勝枚舉,請參閱【Some cool applications of GAN】完整說明。
GAN主要分為兩個網路,一個是偽造者(counterfeiter)就稱為『生成模型』(generative model),另一個稱為『判别模型』(discriminative model),簡單架構如下圖: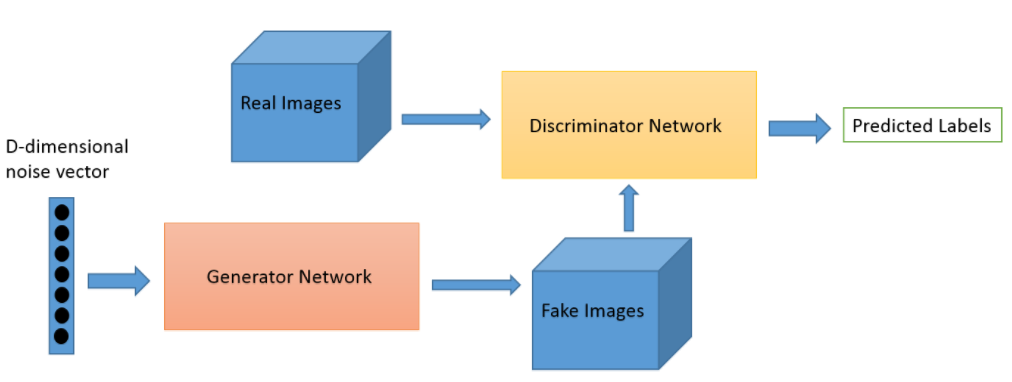
圖. GAN Architecture,圖片來源:generative-adversarial-networks
兩個網路分別定義不同的損失函數,把它合成起來,透過最大概似法(MLE),優化求解,特別的是在『生成模型』求解的過程中,將影像不斷的擷取出來,就構成GAN最大的亮點。各種演算法定義不同的損失函數,就會產生不同的效果,如下表:
接著我們就來實作CycleGAN演算法,將一般的馬加上斑馬紋,看看效果如何。此程式修改自【Keras 官網】,程式碼較長,只說明重要的區塊,完整程式請直接參考 27_01_CycleGAN.ipynb:
dataset, metadata = tfds.load('cycle_gan/horse2zebra',
with_info=True, as_supervised=True)
train_horses, train_zebras = dataset['trainA'], dataset['trainB']
test_horses, test_zebras = dataset['testA'], dataset['testB']
buffer_size = 256
batch_size = 1
# Define the standard image size.
orig_img_size = (286, 286)
# Size of the random crops to be used during training.
input_img_size = (256, 256, 3)
# Weights initializer for the layers.
kernel_init = keras.initializers.RandomNormal(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02)
# Gamma initializer for instance normalization.
gamma_init = keras.initializers.RandomNormal(mean=0.0, stddev=0.02)
def normalize_img(img):
img = tf.cast(img, dtype=tf.float32)
# Map values in the range [-1, 1]
return (img / 127.5) - 1.0
def preprocess_train_image(img, label):
# Random flip
img = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(img)
# Resize to the original size first
img = tf.image.resize(img, [*orig_img_size])
# Random crop to 256X256
img = tf.image.random_crop(img, size=[*input_img_size])
# Normalize the pixel values in the range [-1, 1]
img = normalize_img(img)
return img
def preprocess_test_image(img, label):
# Only resizing and normalization for the test images.
img = tf.image.resize(img, [input_img_size[0], input_img_size[1]])
img = normalize_img(img)
return img
# Apply the preprocessing operations to the training data
train_horses = (
train_horses.map(preprocess_train_image, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
.cache()
.shuffle(buffer_size)
.batch(batch_size)
)
train_zebras = (
train_zebras.map(preprocess_train_image, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
.cache()
.shuffle(buffer_size)
.batch(batch_size)
)
# Apply the preprocessing operations to the test data
test_horses = (
test_horses.map(preprocess_test_image, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
.cache()
.shuffle(buffer_size)
.batch(batch_size)
)
test_zebras = (
test_zebras.map(preprocess_test_image, num_parallel_calls=autotune)
.cache()
.shuffle(buffer_size)
.batch(batch_size)
)
class ReflectionPadding2D(layers.Layer):
"""Implements Reflection Padding as a layer.
Args:
padding(tuple): Amount of padding for the
spatial dimensions.
Returns:
A padded tensor with the same type as the input tensor.
"""
def __init__(self, padding=(1, 1), **kwargs):
self.padding = tuple(padding)
super(ReflectionPadding2D, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def call(self, input_tensor, mask=None):
padding_width, padding_height = self.padding
padding_tensor = [
[0, 0],
[padding_height, padding_height],
[padding_width, padding_width],
[0, 0],
]
return tf.pad(input_tensor, padding_tensor, mode="REFLECT")
# 殘差區塊
def residual_block(
x,
activation,
kernel_initializer=kernel_init,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
strides=(1, 1),
padding="valid",
gamma_initializer=gamma_init,
use_bias=False,
):
dim = x.shape[-1]
input_tensor = x
x = ReflectionPadding2D()(input_tensor)
x = layers.Conv2D(
dim,
kernel_size,
strides=strides,
kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer,
padding=padding,
use_bias=use_bias,
)(x)
x = tfa.layers.InstanceNormalization(gamma_initializer=gamma_initializer)(x)
x = activation(x)
x = ReflectionPadding2D()(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(
dim,
kernel_size,
strides=strides,
kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer,
padding=padding,
use_bias=use_bias,
)(x)
x = tfa.layers.InstanceNormalization(gamma_initializer=gamma_initializer)(x)
x = layers.add([input_tensor, x])
return x
# 下採樣
def downsample(
x,
filters,
activation,
kernel_initializer=kernel_init,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
strides=(2, 2),
padding="same",
gamma_initializer=gamma_init,
use_bias=False,
):
x = layers.Conv2D(
filters,
kernel_size,
strides=strides,
kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer,
padding=padding,
use_bias=use_bias,
)(x)
x = tfa.layers.InstanceNormalization(gamma_initializer=gamma_initializer)(x)
if activation:
x = activation(x)
return x
# 上採樣
def upsample(
x,
filters,
activation,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
strides=(2, 2),
padding="same",
kernel_initializer=kernel_init,
gamma_initializer=gamma_init,
use_bias=False,
):
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(
filters,
kernel_size,
strides=strides,
padding=padding,
kernel_initializer=kernel_initializer,
use_bias=use_bias,
)(x)
x = tfa.layers.InstanceNormalization(gamma_initializer=gamma_initializer)(x)
if activation:
x = activation(x)
return x
建立生成模型(generators)結構如下,程式請參考 27_01_CycleGAN.ipynb:
建立判別模型(discriminators),程式請參考 27_01_CycleGAN.ipynb。
連接生成模型與判別模型,建立CycleGAN 模型。
建立 callback,在每一執行週期結束將生成的影像存檔。
訓練模型,同時產生影像。
結果如下,真的把馬加上紋路了。
除了GAN以外,還有許多演算法可以生成影像,例如:
GAN 除了有娛樂效果外,還可以生成訓練資料(類似資料增補)、醫療影像等較正規的用途,它是一個很迷人的領域,不過,要深入研究,恐怕要投資一張不錯的獨立顯卡,否則光訓練時間,就可以等到變化石了。
本篇範例包括 27_01_CycleGAN.ipynb,可自【這裡】下載。
