昨天拿computed跟methods做比較,今天換來跟watch比比看過五關斬六將ヾ(´︶`*)ノ♬
大部分情況可以用computed,但如果是非同步、消耗較大較複雜的操作比較適合用watch。
Watch沒有cache的機制,但有連動的概念,資料產生行為,資料觸發行為(資料變了會去呼叫function),比較不適合單純處理普通資料(資料馬上產出資料比較適合用computed),算是萬用型但容易被濫用。
下面的範例我們用 v-model 綁定 input 的值為 question,當我們在輸入問題的時候,watch 裡面的 question function會執行,methods裡的getAnswer也會執行,再送出 AJAX 去取得答案傳回來。
this.debouncedGetAnswer = _.debounce(this.getAnswer, 500)
這裡使用了 lodash.js 的 debounce 函式,設定在使用者輸入停止 500 毫秒的時候,會先確認有沒有問號,接著才發送 AJAX 去取得問題的答案,目的是為了避免使用者在輸入完問題之前,就發送不必要的 Request。
<div id="app">
<p>
Ask a yes/no question:
<input v-model="question">
</p>
<p>{{ answer }}</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.12.0/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/lodash@4.13.1/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
question: '',
answer: 'I cannot give you an answer until you ask a question!'
},
watch: {
// 如果 `question` 發生改變,這個函數就會運行
question: function (newQuestion, oldQuestion) {
this.answer = 'Waiting for you to stop typing...'
this.debouncedGetAnswer()
}
},
created: function () {
this.debouncedGetAnswer = _.debounce(this.getAnswer, 500)
},
methods: {
getAnswer: function () {
if (this.question.indexOf('?') === -1) {
this.answer = 'Questions usually contain a question mark. ;-)'
return
}
this.answer = 'Thinking...'
var vm = this
axios.get('https://yesno.wtf/api')
.then(function (response) {
vm.answer = _.capitalize(response.data.answer)
})
.catch(function (error) {
vm.answer = 'Error! Could not reach the API. ' + error
})
}
}
});
</script>
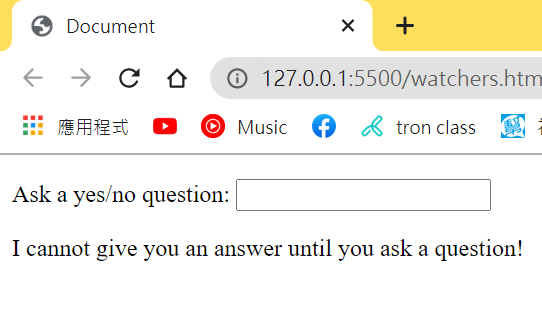
一開始我們還沒輸入問題的時候,它會跳出”I cannot give you an answer until you ask a question! 就是叫你趕快給我問問題喇
在打字的時候會跳出”Waiting for you to stop typing…”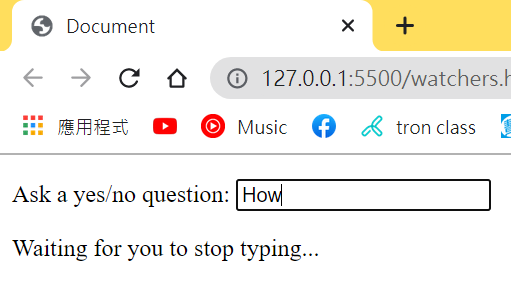
當我們打好字停下來,它會判斷有沒有問號,沒有的話會跟你說問問題要包含問號歐(´▽`ʃ♡ƪ)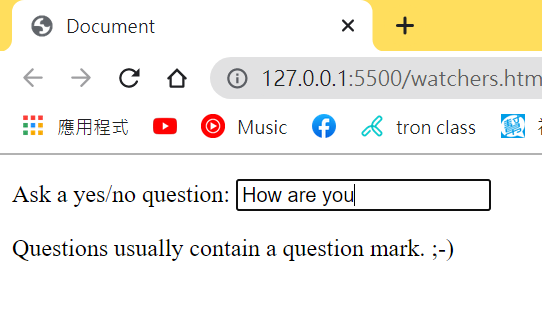
打完問題(加上問號)他會先思考思考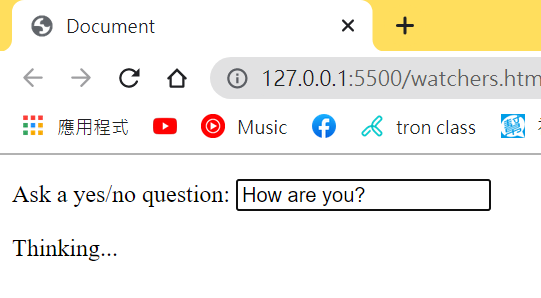
看來它今天過得不太好இдஇ 沒事喇 我也不太好( ´・・)ノ(._.`)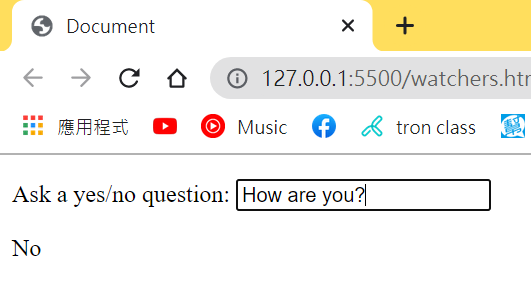
<div id="app">
<p>computed:{{ fullName }}</p>
<p>watch:{{fullNameWatch}}</p>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar',
fullNameWatch: 'Foo Bar' // watch 需手動設置初始值
},
computed: {
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
},
watch: {
firstName: function (val) {
this.fullNameWatch = this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
},
lastName: function (val) {
this.fullNameWatch = this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
}
});
</script>
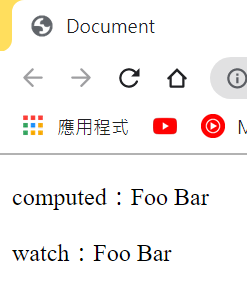
我們可以看到兩者呈現的結果是一樣的
但watch的程式碼事命令式且重複,所以在這個例子中比要適合用computed,較精簡也較好懂(「・ω・)「