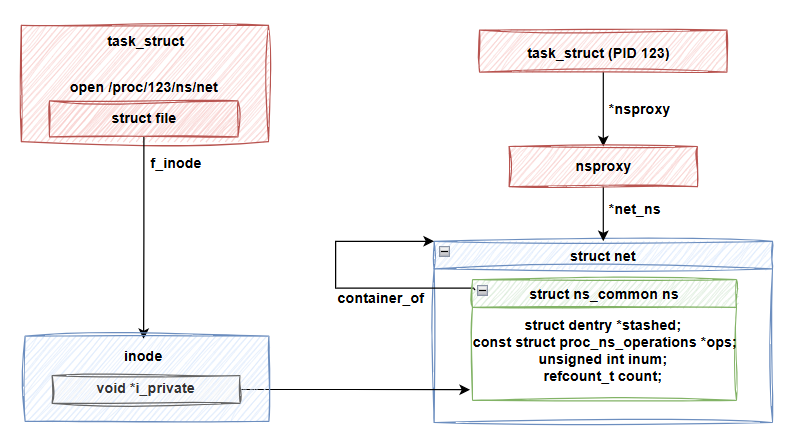
昨天我們探討了 setns 的整個實作流程,並發現 process 123 使用的 network namespace 結構 (net) 的 ns_common 會保存在當我們打開 /proc/123/ns/net 時,透過 file->f_inode->i_private 取得。我們今天就要進一步了解,這個關聯是如何建立的。
/proc/<pid>/ns 目錄的生成機制首先,我們需要檢視 proc 檔案系統是如何生成 /proc/<pid>/ns 目錄的。
// proc/base.c
static const struct pid_entry tgid_base_stuff[] = {
DIR("task", S_IRUGO|S_IXUGO, proc_task_inode_operations, proc_task_operations),
DIR("fd", S_IRUSR|S_IXUSR, proc_fd_inode_operations, proc_fd_operations),
DIR("map_files", S_IRUSR|S_IXUSR, proc_map_files_inode_operations, proc_map_files_operations),
DIR("fdinfo", S_IRUGO|S_IXUGO, proc_fdinfo_inode_operations, proc_fdinfo_operations),
DIR("ns", S_IRUSR|S_IXUGO, proc_ns_dir_inode_operations, proc_ns_dir_operations),
#ifdef CONFIG_NET
DIR("net", S_IRUGO|S_IXUGO, proc_net_inode_operations, proc_net_operations),
#endif
REG("comm", S_IRUGO|S_IWUSR, proc_pid_set_comm_operations),
...
可以看到,ns 是一個目錄,且其 inode_operations 是 proc_ns_dir_inode_operations,file_operations 則是 proc_ns_dir_operations。
因此,當我們打開 /proc/123/ns/net 時,會呼叫 proc_ns_dir_inode_operations.lookup 來建立/proc/123/ns/net 的 dentry 和 inode。
// fs/proc/namespaces.c
static struct dentry *proc_ns_dir_lookup(struct inode *dir,
struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags)
{
struct task_struct *task = get_proc_task(dir); // 取得 process 123 的 task_struct
const struct proc_ns_operations **entry, **last;
unsigned int len = dentry->d_name.len;
struct dentry *res = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
last = &ns_entries[ARRAY_SIZE(ns_entries)];
for (entry = ns_entries; entry < last; entry++) {
if (strlen((*entry)->name) != len)
continue;
if (!memcmp(dentry->d_name.name, (*entry)->name, len)) // 找到 name 為 net 的 entry
break;
}
if (entry == last)
goto out;
res = proc_ns_instantiate(dentry, task, *entry); // 執行 proc_ns_instantiate
out:
put_task_struct(task);
out_no_task:
return res;
}
這段 lookup 函數相當複雜,我們可以分段解析:
/proc/123/ns 的 inode 和 /proc/123/ns/net 的空 dentry。get_proc_task 取得 process 123 的 task_struct,並將其保存到 task。ns_entries 陣列中找到一個名稱為 net 的 entry。/proc/123/ns/net 的空 dentry、task_struct 和找到的 entry 傳遞給 proc_ns_instantiate 處理。static const struct proc_ns_operations *ns_entries[] = {
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS
&netns_operations, // network namespace
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_UTS_NS
&utsns_operations,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IPC_NS
&ipcns_operations,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PID_NS
&pidns_operations,
&pidns_for_children_operations,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_USER_NS
&userns_operations,
#endif
&mntns_operations,
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
&cgroupns_operations,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TIME_NS
&timens_operations,
&timens_for_children_operations,
#endif
};
這裡的 entry 就是昨天介紹過的 proc_ns_operations,而 netns_operations 則是專門用於處理 network namespace 的操作結構。
// net/core/net_namespace.c
const struct proc_ns_operations netns_operations = {
.name = "net",
.type = CLONE_NEWNET,
.get = netns_get,
.put = netns_put,
.install = netns_install,
.owner = netns_owner,
};
其中 netns_operations,就是昨天介紹由 network namespace 系統定義的,當然他的 name 欄位就對應到 net。
回到 proc_ns_dir_lookup,最終呼叫 proc_ns_instantiate,將 /proc/123/ns/net 的 dentry、process 123 和 netns_operations 傳入進行進一步處理。
// fs/proc/namespaces.c
static struct dentry *proc_ns_instantiate(struct dentry *dentry,
struct task_struct *task, const void *ptr)
{
const struct proc_ns_operations *ns_ops = ptr; // netns_operations
struct inode *inode;
struct proc_inode *ei;
inode = proc_pid_make_inode(dentry->d_sb, task, S_IFLNK | S_IRWXUGO); // 軟連結
if (!inode)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
ei = PROC_I(inode);
inode->i_op = &proc_ns_link_inode_operations; // 設置 inode_operations
ei->ns_ops = ns_ops;
pid_update_inode(task, inode);
d_set_d_op(dentry, &pid_dentry_operations);
return d_splice_alias(inode, dentry);
}
proc_ns_instantiate 實現的是 lookup 函數的邏輯,我們可以關注幾個重點:
S_IFLNK(symbolic link)軟連結檔案。i_op (inode_operations) 是 proc_ns_link_inode_operations。ns_ops(即 netns_operations)會被保存到 ei->ns_ops,struct proc_inode {
struct pid *pid;
unsigned int fd;
union proc_op op;
struct proc_dir_entry *pde;
struct ctl_table_header *sysctl;
struct ctl_table *sysctl_entry;
struct hlist_node sibling_inodes;
const struct proc_ns_operations *ns_ops;
struct inode vfs_inode;
} __randomize_layout;
proc_inode 是 proc 設計的一個擴充的 inode 結構,用來保存 proc 檔案系統需要的 process 資訊 (task_struct) 等,也將 VFS 的 inode 結構內嵌在 proc_inode 裡面。當透過 proc_pid_make_inode 申請一個 inode 時,實際上建立的是 proc_inode 實例,然後返回子結構 vfs_inode。所以 PROC_I macro 可以透過 container_of 拿到外層的 proc_inode 結構。
所以可以發現 /proc/123/ns/net是一個 symbolic link 檔案,對於軟連結檔案,你透過 open system call 打開時,最終 file 結構指向不是打開的那個檔案,而是連結的目標檔案。
在 Linux 的檔案系統中,symbolic link 是一種特殊的檔案類型,透過它可以連結到其他檔案。對於 symbolic link 檔案,相關的 inode 具有兩個重要的函數:readlink 和 get_link。
static const struct inode_operations proc_ns_link_inode_operations = {
.readlink = proc_ns_readlink,
.get_link = proc_ns_get_link,
.setattr = proc_setattr,
};
int (*readlink) (struct dentry *, char __user *,int);
const char * (*get_link) (struct dentry *, struct inode *, struct delayed_call *);
readlink 的功能是取得該 symbolic link 所指向的檔案名稱。
> ls /proc/1/ns -l
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 cgroup -> 'cgroup:[4026531835]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 ipc -> 'ipc:[4026531839]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 mnt -> 'mnt:[4026531840]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 net -> 'net:[4026531992]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 pid -> 'pid:[4026531836]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 pid_for_children -> 'pid:[4026531836]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 user -> 'user:[4026531837]'
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 九 19 22:02 uts -> 'uts:[4026531838]'
ls 指令看到的 net:[4026531992] ,就致 net 這個 symbolic link 檔案連結過去的檔案名稱。
接下來,我們來探討 /proc/123/ns/net inode 使用的 proc_ns_readlink 函數是如何取得 symbolic link 的目標檔案名稱。
static int proc_ns_readlink(struct dentry *dentry, char __user *buffer, int buflen)
{
struct inode *inode = d_inode(dentry);
const struct proc_ns_operations *ns_ops = PROC_I(inode)->ns_ops;
struct task_struct *task;
char name[50];
int res = -EACCES;
task = get_proc_task(inode); // 從 inode 拿到 proc_inode,然後取得 process 123 的 task_struct
...
res = ns_get_name(name, sizeof(name), task, ns_ops);
...
}
在這段程式碼中,proc_ns_readlink 函數首先從 inode 取得與該 inode 關聯的 task_struct,並呼叫 ns_get_name 函數來取得目標檔案的名稱。ns_get_name 函數的定義位於 fs/nsfs.c。
終於我們要進入到今天的另外一個主角 NameSpace File System (NSFS)。這個是 Linux 專門針對 /proc/123/ns/net 這類指向 namespace 結構的檔案專門設計的檔案系統。
特別注意,我使用的 kernel版本是 6.6.47,從 6.6.47 到最新的 6.11 中間,nsfs 檔案系統的程式碼有大幅度修改,函數名稱和實作內容都有蠻大的變化。
NSFS 是一種特殊的虛擬檔案系統,具有以下幾個特性:
inode 的 i_private 會指向該 namespace 實例的 ns_common 結構體。/proc/<pid>/ns/* 軟連結對應的檔案。這個掛起來的檔案系統,只是在 kernel 有對應的 vfsmount 掛載資料結構存在,但沒有掛載到 VFS 檔案樹上面,所以並沒有路徑可以直接找到這個預設的 NSFS 檔案系統,mount 指令也看不到。<namespace type>:<inode number>,使用 proc_ns_operations.name 作為 namespace type,然後使用 ns_common 結構的 inum 作為 inode numberls /proc/123/ns/net 會顯示檔名 net:[4026531992]。下圖說明了打開 /proc/123/ns/net後, NSFS 的運作方式:
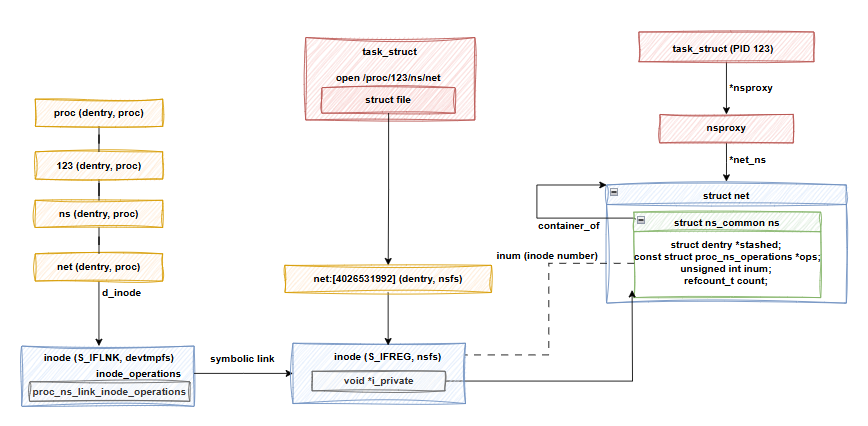
在這張圖中,我們可以看到 /proc/123/ns/net 是一個 symbolic link 檔案,透過 open 系統呼叫會 "follow" 到 net:[4026531992],並取得對應的 ns_common 結構。
前面說到 proc_ns_readlink 會呼叫 ns_get_name 函數來取得 NSFS 檔案的名稱:
// fs/nsfs.c
int ns_get_name(char *buf, size_t size, struct task_struct *task,
const struct proc_ns_operations *ns_ops) // 傳入 netns_operations
{
struct ns_common *ns;
int res = -ENOENT;
const char *name;
ns = ns_ops->get(task); // proc_ns_operations GET API
if (ns) {
name = ns_ops->real_ns_name ? : ns_ops->name;
res = snprintf(buf, size, "%s:[%u]", name, ns->inum); // net:[4026531992]
ns_ops->put(ns);
}
return res;
}
從這段程式碼可以看出,NSFS 的檔案名稱是動態產生的,而非從某個 dentry 讀取出來的。這裡使用 ns_ops.name 取得 namespace 的類型名稱 (例如 net),並使用 ns_ops->get 取得對應的 ns_common 結構,最終將 ns->inum 作為 inode number。
我們可以從這裡發現這真的是一個純虛擬的檔案系統,他的檔案名稱直接是造出來的,而不是從某個 dentry 讀出來的,這邊會透過輸入的 ns_ops.name 拿到 namespace 的類型名稱 (net),然後透過其面介紹的ns_ops->get 拿到對應namepsace類型的ns_common結構,這邊是使用net的ns_ops,所以就會拿到 network namespace的ns_common,然後就真的用 ns->inum當作inode number了。
透過前面的探討,我們瞭解到,當我們打開 /proc/123/ns/net 時,/proc/123/ns/net 會軟連結到 NSFS 檔案系統中,代表 prcess 123 使用的 network namespace 的檔案。明天,我們將進一步探討打開 /proc/123/ns/net 時,系統是如何將 file 結構連結到 NSFS 檔案的,並瞭解 NSFS 檔案的 dentry 與 inode 是如何產生的。
