上一篇自行開發梯度下降法找到最佳解,這次我們使用TensorFlow低階API進行自動微分(Automatic Differentiation),並實作多元線性迴歸。
從下圖可以了解,神經網路求解會使用到張量(Tensor)運算及偏微分...等,因此,所有深度學習套件除了支援神經網路的建構外,基本上都會支援張量(Tensor)運算及自動微分(Automatic Differentiation),以減輕開發者的負擔。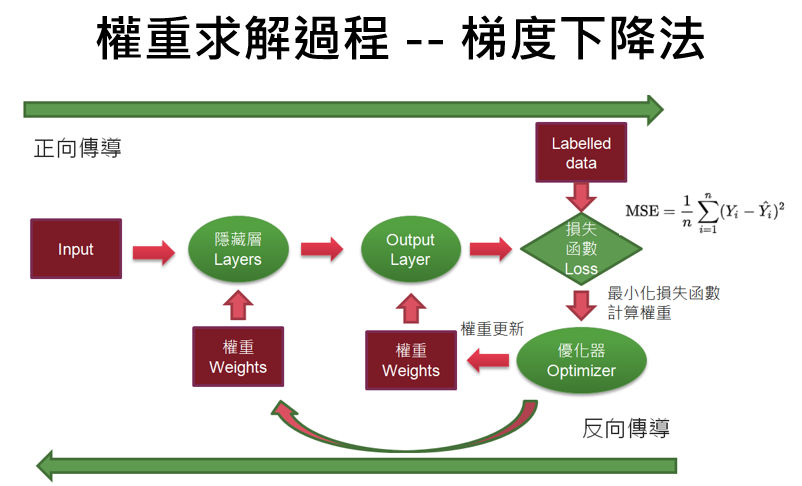
圖一. 梯度下降法的權重求解過程
不使用 model.fit而改用自動微分,可以掌控模型訓練的過程,也可以取得更多的資訊,例如:
像PyTorch、Jax...等深度學習套件就不支援model.fit,強制開發者必須要依圖一流程,訓練模型。
範例1. 自動微分測試,對y=x²自動微分。
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.Variable(3.0) # 宣告 TensorFlow 變數(Variable)
with tf.GradientTape() as g: # 自動微分
y = x * x # 損失函數
dy_dx = g.gradient(y, x) # 取得梯度, f'(x) = 2x, x=3 ==> 6
print(dy_dx.numpy()) # 轉換為 NumPy array 格式
x = tf.Variable(3.0) # 宣告 TensorFlow 變數(Variable)
with tf.GradientTape() as g: # 自動微分
y = x * tf.sin(x) ** 2 # 損失函數
dy_dx = g.gradient(y, x) # 取得梯度, f'(x) = 2x, x=3 ==> 6
print(dy_dx.numpy()) # 轉換為 NumPy array 格式
範例2. 再測試 PyTorch 深度學習套件的自動微分功能,同樣對y=x²自動微分。
import torch
x = torch.tensor(3.0, requires_grad=True) # 設定 x 參與自動微分
y=x*x # 損失函數
y.backward() # 反向傳導
print(x.grad.numpy()) # 取得梯度
範例3. 以上篇為例,以自動微分對y=x²求解最小值。
def train(w_start, epochs, lr):
w_list = np.array([])
w = tf.Variable(w_start) # 宣告 TensorFlow 變數(Variable)
w_list = np.append(w_list, w_start)
# 執行N個訓練週期
for i in range(epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as g: # 自動微分
y = w * w # 損失函數
dw = g.gradient(y, w) # 取得梯度
# 更新權重:新權重 = 原權重 — 學習率(learning_rate) * 梯度(gradient)
w.assign_sub(lr * dw) # w -= dw * lr
w_list = np.append(w_list, w.numpy())
return w_list
# 載入套件
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
import tensorflow as tf
# 修正中文亂碼
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft JhengHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 損失函數為 y=x^2
def func(x): return x ** 2
# @tf.function
def train(w_start, epochs, lr):
w_list = np.array([])
w = tf.Variable(w_start) # 宣告 TensorFlow 變數(Variable)
w_list = np.append(w_list, w_start)
# 執行N個訓練週期
for i in range(epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as g: # 自動微分
y = w * w # 損失函數
dw = g.gradient(y, w) # 取得梯度
# 更新權重:新權重 = 原權重 — 學習率(learning_rate) * 梯度(gradient)
w.assign_sub(lr * dw) # w -= dw * lr
w_list = np.append(w_list, w.numpy())
return w_list
# 模型訓練:呼叫梯度下降法
w_start = -5.0 # 權重初始值
epochs = 150 # 訓練週期數
lr = 0.1 # 學習率
w_list = train(w_start, epochs, lr=lr)
print (f'w:{np.around(w_list, 2)}')
# 繪圖觀察權重更新過程
color = 'r'
t = np.arange(-6.0, 6.0, 0.01)
plt.plot(t, func(t), c='b')
plt.plot(w_list, func(w_list), c=color, label='lr={}'.format(lr))
plt.scatter(w_list, func(w_list), c=color)
# 繪圖箭頭,顯示權重更新方向
plt.quiver(w_list[0]-0.2, func(w_list[0]), w_list[4]-w_list[0],
func(w_list[4])-func(w_list[0]), color='g', scale_units='xy', scale=5)
# 繪圖標題設定
font = {'family': 'Microsoft JhengHei', 'weight': 'normal', 'size': 20}
plt.title('梯度下降法', fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('w', fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel('Loss', fontsize=20)
plt.show()
上面範例只考慮w,若加上偏差項b,即 y = wx + b,要如何實作呢?
範例3. 一元線性迴歸。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
X1, y= make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=15, bias=50)
X=X1.ravel() # 轉為一維陣列
# 設定圖形更新的頻率
PAUSE_INTERVAL=0.5
# 設定圖形大小
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(10, 6)
# 繪製亂數資料散佈圖
plt.scatter(X,y)
line, = ax.plot(X, [0] * len(X), 'r')
# 求預測值(ŷ)
def predict(X):
return w * X + b
# 計算損失函數 MSE = ∑(y-ŷ)**2/n
def loss(y, y_pred):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_pred))
def draw(w, b):
# 更新圖形Y軸資料
y_new = [b + w * xplot for xplot in X]
line.set_data(X, y_new) # update the data.
#ax.cla()
plt.pause(PAUSE_INTERVAL)
def train(X, y, epochs=40, lr=0.1):
current_loss=0 # 損失函數值
for epoch in range(epochs): # 執行訓練週期
with tf.GradientTape() as t: # 自動微分
t.watch(tf.constant(X)) # 宣告 TensorFlow 常數參與自動微分
current_loss = loss(y, predict(X)) # 計算損失函數值
dw, db = t.gradient(current_loss, [w, b]) # 取得 w, b 個別的梯度
# 更新權重:新權重 = 原權重 — 學習率(learning_rate) * 梯度(gradient)
w.assign_sub(lr * dw) # w -= lr * dw
b.assign_sub(lr * db) # b -= lr * db
# 更新圖形
draw(w, b)
# 顯示每一訓練週期的損失函數
print(f'Epoch {epoch}: Loss: {current_loss.numpy()}')
# w、b 初始值均設為 0
w = tf.Variable(0.0)
b = tf.Variable(0.0)
# 執行訓練
train(X, y)
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X1, y)
print(f'w={model.coef_[0]}, b={model.intercept_}')
# 載入套件
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
# 生成亂數資料
X1, y= make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=15, bias=50)
X=X1.ravel() # 轉為一維陣列
# print(X, y)
# 設定圖形更新的頻率
PAUSE_INTERVAL=0.5
# 設定圖形大小
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fig.set_size_inches(10, 6)
# 繪製亂數資料散佈圖
plt.scatter(X,y)
line, = ax.plot(X, [0] * len(X), 'r')
# 求預測值(Y hat)
def predict(X):
return w * X + b
# 計算損失函數 MSE = ∑(y-ŷ)**2/n
def loss(y, y_pred):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_pred))
# 定義繪製迴歸線的函數
def draw(w, b):
# 更新圖形Y軸資料
y_new = [b + w * xplot for xplot in X]
line.set_data(X, y_new) # update the data.
#ax.cla()
plt.pause(PAUSE_INTERVAL)
# 定義訓練函數
def train(X, y, epochs=40, lr=0.1):
current_loss=0 # 損失函數值
for epoch in range(epochs): # 執行訓練週期
with tf.GradientTape() as t: # 自動微分
t.watch(tf.constant(X)) # 宣告 TensorFlow 常數參與自動微分
current_loss = loss(y, predict(X)) # 計算損失函數值
dw, db = t.gradient(current_loss, [w, b]) # 取得 w, b 個別的梯度
# 更新權重:新權重 = 原權重 — 學習率(learning_rate) * 梯度(gradient)
w.assign_sub(lr * dw) # w -= lr * dw
b.assign_sub(lr * db) # b -= lr * db
# 更新圖形
draw(w, b)
# 顯示每一訓練週期的損失函數
print(f'Epoch {epoch}: Loss: {current_loss.numpy()}')
# 模型訓練
# w、b 初始值均設為 0
w = tf.Variable(0.0)
b = tf.Variable(0.0)
# 執行訓練
train(X, y)
# w、b 的最佳解
print(f'w={w.numpy()}, b={b.numpy()}')
# 顯示動畫
# plt.show()
# 驗證 w、b是否正確:使用Scikit-learn套件比對
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X1, y)
print(f'w={model.coef_[0]}, b={model.intercept_}')
執行:python 10_簡單線性迴歸_自動微分.py。
執行結果:w、b逐步更新,最終迴歸線自亂數資料中間穿過。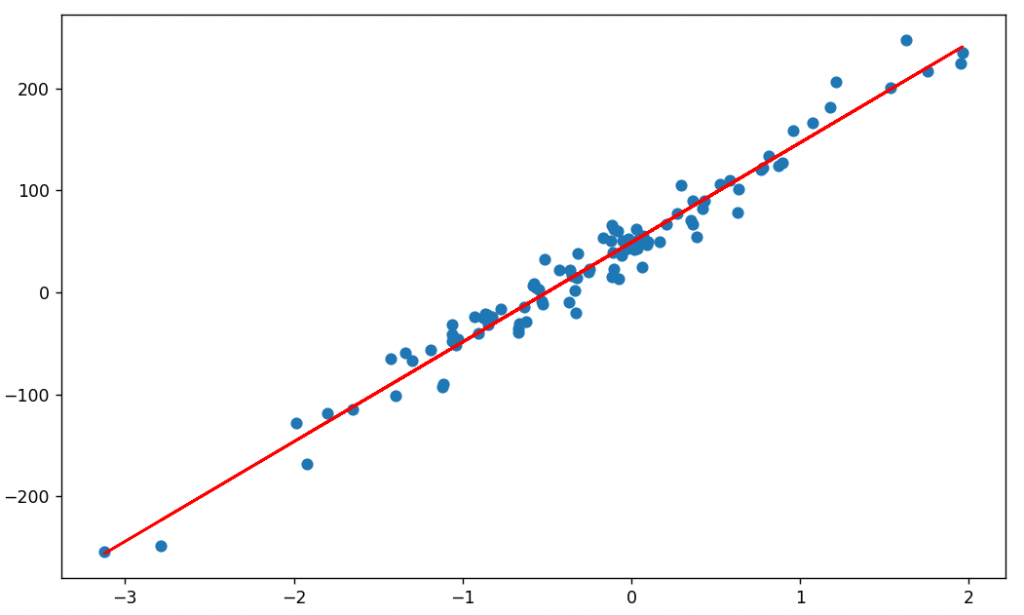
驗證 w、b:與Scikit-learn套件計算結果非常相近。
梯度下降法:w=87.38388061523438, b=48.79069519042969
Scikit-learn:w=87.39229369, b=48.788610878339966
X, y= make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=2, noise=15, bias=50)
本篇介紹以自動微分(Automatic Differentiation)實作梯度下降,下一篇我們介紹一些應用,不限於神經網路:
Happy coding !!
徹底理解神經網路的核心 -- 梯度下降法 (1)
徹底理解神經網路的核心 -- 梯度下降法 (2)
徹底理解神經網路的核心 -- 梯度下降法 (3)
徹底理解神經網路的核心 -- 梯度下降法 (4)
徹底理解神經網路的核心 -- 梯度下降法的應用 (5)
梯度下降法(6) -- 學習率動態調整
梯度下降法(7) -- 優化器(Optimizer)
梯度下降法(8) -- Activation Function
梯度下降法(9) -- 損失函數
梯度下降法(10) -- 總結
