我們直接上圖: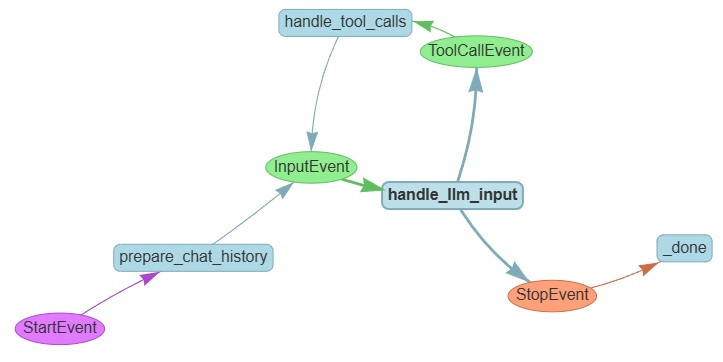
1.1 [event] StartEvent: input 裡面放的是 user 本輪問的問題
1.2 [step] prepare_chat_history: 這個主要做兩件事
1.3 [event] InputEvent: input 裡面放的是 chat_history
1.4 [step] handle_llm_input: 這個主要就是去用 chat_history 呼叫 llm
1.5 [event] ToolCallEvent: tool_calls 裡面放的是 list of ToolSelection
1.6 [step] handle_tool_calls: 就是幫 llm 去 call tool
1.7 [event] StopEvent: result 放的是 dictionary
import os
from dotenv import find_dotenv, load_dotenv
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
from llama_index.core.llms import ChatMessage
from llama_index.core.workflow import Event
from typing import Any, List
from llama_index.core.llms.function_calling import FunctionCallingLLM
# from llama_index.core.memory import ChatMemoryBuffer
from llama_index.core.memory import Memory
from llama_index.core.tools import ToolSelection, ToolOutput
from llama_index.core.tools.types import BaseTool
from llama_index.core.workflow import (
Context,
Workflow,
StartEvent,
StopEvent,
step,
)
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.utils.workflow import draw_all_possible_flows
from llama_index.core.memory import Memory
class InputEvent(Event):
input: list[ChatMessage]
class ToolCallEvent(Event):
tool_calls: list[ToolSelection]
class FunctionOutputEvent(Event):
output: ToolOutput
class StreamEvent(Event):
msg: ChatMessage
class FunctionCallingAgent(Workflow):
def __init__(
self,
*args: Any,
llm: FunctionCallingLLM | None = None,
tools: List[BaseTool] | None = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.tools = tools or []
self.llm = llm or OpenAI()
assert self.llm.metadata.is_function_calling_model
跟 Day13 不一樣,這次就把該用的都放在 init 了
4.2 prepare_chat_history
@step
async def prepare_chat_history(
self, ctx: Context, ev: StartEvent
) -> InputEvent:
# clear sources
await ctx.store.set("sources", [])
# check if memory is setup
memory = await ctx.store.get("memory", default=None)
if not memory:
#memory = ChatMemoryBuffer.from_defaults(llm=self.llm)
memory = Memory.from_defaults(token_limit=40000)
# get user input
user_input = ev.input
user_msg = ChatMessage(role="user", content=user_input)
memory.put(user_msg)
# get chat history
chat_history = memory.get()
# update context
await ctx.store.set("memory", memory)
return InputEvent(input=chat_history)
這個 sources 放的是 所有 tool 呼叫的結果,每次會先清空
memory 的部分如前述
4.3 handle_llm_input
@step
async def handle_llm_input(
self, ctx: Context, ev: InputEvent
) -> ToolCallEvent | StopEvent:
chat_history = ev.input
# stream the response
#response_stream = await self.llm.astream_chat_with_tools(
# self.tools, chat_history=chat_history
#)
response = await self.llm.achat_with_tools(
self.tools, chat_history=chat_history
)
ctx.write_event_to_stream(StreamEvent(msg=response.message))
# save the final response, which should have all content
memory = await ctx.store.get("memory")
memory.put(response.message)
await ctx.store.set("memory", memory)
# get tool calls
tool_calls = self.llm.get_tool_calls_from_response(
response, error_on_no_tool_call=False
) # 如果這邊沒有 tool calls 回傳就會是 []
if not tool_calls:
sources = await ctx.store.get("sources", default=[])
return StopEvent(
result={"response": response, "sources": [*sources]}
)
else:
return ToolCallEvent(tool_calls=tool_calls)
這邊要看的是回傳型別是 ToolCallEvent | StopEvent
有分支的 workflow 就是這樣做出來的
workflow 跟 visualize 是靠回傳型別知道要執行哪個 step 的
然後要注意的是這邊是呼叫 llm.achat_with_tools
llm.get_tool_calls_from_response 回傳的是 list of ToolSelection
4.4 handle_tool_calls
@step
async def handle_tool_calls(
self, ctx: Context, ev: ToolCallEvent
) -> InputEvent:
tool_calls = ev.tool_calls # model 要 call 的 tool
tools_by_name = {tool.metadata.get_name(): tool for tool in self.tools} # 可以使用的 tool
tool_msgs = []
sources = await ctx.store.get("sources", default=[])
# call tools -- safely!
for tool_call in tool_calls:
tool = tools_by_name.get(tool_call.tool_name)
additional_kwargs = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call.tool_id,
"name": tool.metadata.get_name(),
}
if not tool:
tool_msgs.append(
ChatMessage(
role="tool",
content=f"Tool {tool_call.tool_name} does not exist",
additional_kwargs=additional_kwargs,
)
)
continue
try:
tool_output = tool(**tool_call.tool_kwargs)
sources.append(tool_output)
tool_msgs.append(
ChatMessage(
role="tool",
content=tool_output.content,
additional_kwargs=additional_kwargs,
)
)
except Exception as e:
tool_msgs.append(
ChatMessage(
role="tool",
content=f"Encountered error in tool call: {e}",
additional_kwargs=additional_kwargs,
)
)
# update memory
memory = await ctx.store.get("memory")
for msg in tool_msgs:
memory.put(msg)
await ctx.store.set("sources", sources)
await ctx.store.set("memory", memory)
chat_history = memory.get()
return InputEvent(input=chat_history)
draw_all_possible_flows(
FunctionCallingAgent, filename="day14_FunctionCallingAgent.html"
)
from llama_index.tools.tavily_research.base import TavilyToolSpec
TAVILY_API_KEY = os.getenv("TAVILY_API_KEY")
tavily_tool = TavilyToolSpec(
api_key=TAVILY_API_KEY,
)
tools = tavily_tool.to_tool_list()
# 把工具轉成文字
tool_descs = []
for tool in tools:
tool_descs.append(f"{tool.metadata.name}: {tool.metadata.description}")
tools_str = "\n".join(tool_descs)
tools_str
name 跟 description
search: search(query: str, max_results: Optional[int] = 6) -> List[llama_index.core.schema.Document]
Run query through Tavily Search and return metadata.
agent = FunctionCallingAgent(
llm=OpenAI(model="gpt-5-mini", is_streaming=False), tools=tools, timeout=120, verbose=True
)
ret = await agent.run(input="Hello!")
我們今天嘗試用 workflow 來把 FunctionCallingAgent 寫出來
我們學會了架設有分支的 workflow
而且這個隨著問不同的問題,真的不知道到底會跑多少 step
學了基礎的 memory 使用
還有釐清了 FunctionCallingAgent 的呼叫細節
明天來實作 ReAct Agent 跟今天可以有個具體的比較
