在 Day 5 我們學會了如何抓取 Notion Database 的 Schema 與 rows,並將其清洗成乾淨的 JSON。但光是抓到 Database 還不夠,因為 Database 內的每一筆 row,都可能有更豐富的內容(Page):課程筆記、代碼範例、重點摘要等。
如果能透過 API 把這些 Block 轉換成結構化且乾淨的 JSON,我們就能做更多進一步的應用:
👉 本篇目標:
Database → Page → Block 的階層結構。Page 與 Block 的內容。我在 Notion 建立了一個 inline database:Python_Basic,主要用來整理 Python Basic 的學習重點,本篇會以這個學習筆記示範如何抓取Page 與 Block 的內容。
ScopeName:主題名稱,例如 Variables、Data TypesStatus:學習進度(Todo / In Progress / Done)
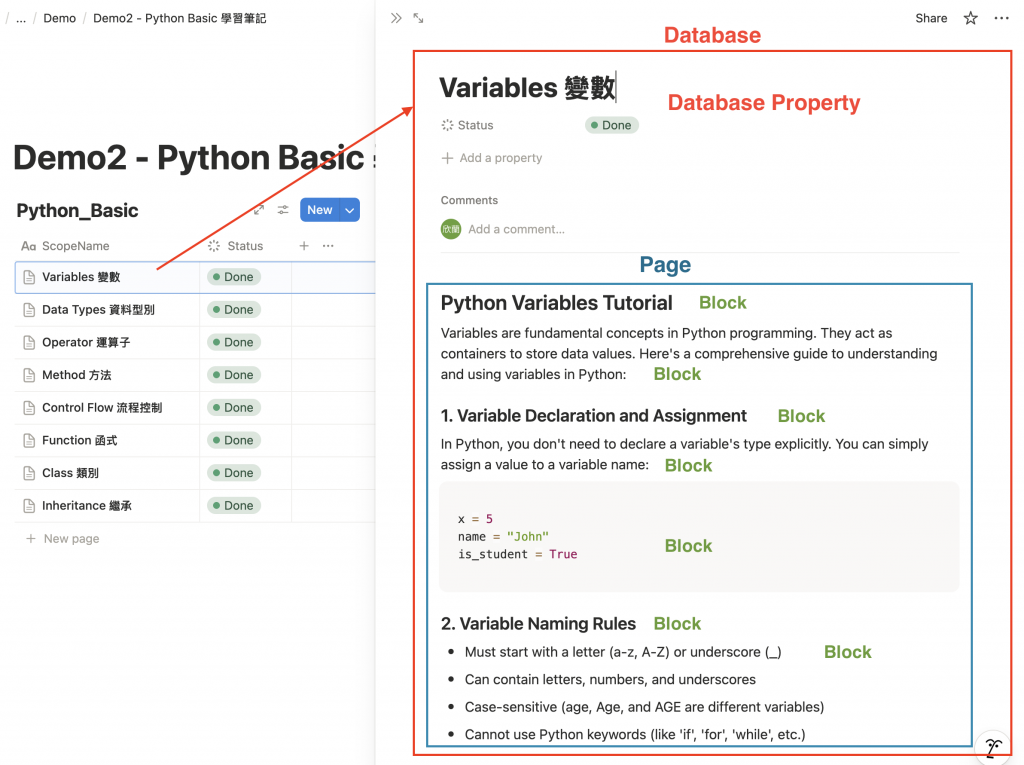
Database 中的每個 row 背後其實就是一個獨立的 Page。Variables 變數,會看到:
x = 5
name = "John"
is_student = True
在 Notion API 裡,這三個概念的關係如下:
Page。Database 的一筆資料(row)其實就是一個 Page,可以打開看到詳細內容。Page 內的最小單位(文字、圖片、代碼區塊、todo list 都是 Block)。以我們的範例資料來說,結構大致會是這樣:
Database: Python_Basic
└── Page: Variables 變數
├── Block: 標題 "Python Variables Tutorial"
├── Block: 文字敘述
├── Block: 程式碼區塊
└── Block: 清單項目
如果你想更直觀理解 Block,可以參考官方文件:
👉 Block basics: build the foundation for your team’s pages
延續 Day 5 的程式,我們已經能取得 Database rows,每一筆 row 會有一個 page_id,接下來,我們就可以利用這個 page_id 去抓 Page 的內容。
POST https://api.notion.com/v1/databases/{database_id}/query
start_cursor 搭配 has_more 參數來一次抓完所有 rows。fetch_learning_database.py 程式碼
import requests, os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
TOKEN = os.getenv("NOTION_TOKEN")
BASE = "https://api.notion.com/v1"
HEADERS = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {TOKEN}",
"Notion-Version": "2022-06-28",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
def query_database_all(database_id: str, page_size: int = 100) -> list:
url = f"{BASE}/databases/{database_id}/query"
payload, results = {"page_size": page_size}, []
while True:
res = requests.post(url, headers=HEADERS, json=payload)
res.raise_for_status()
data = res.json()
results.extend(data.get("results", []))
if not data.get("has_more"):
break
payload["start_cursor"] = data["next_cursor"]
return results
GET https://api.notion.com/v1/blocks/{block_id}/children
Block 是 Page 的最小單位(文字、標題、程式碼、清單...)。Block 可能有子層 (has_children=true),必須用遞迴方式展開。paragraph
heading_1/2/3
code
to_do
bulleted_list_item / numbered_list_item
fetch_learning_blocks.py 程式碼:
import os, requests
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
TOKEN = os.getenv("NOTION_TOKEN")
BASE = "https://api.notion.com/v1"
HEADERS = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {TOKEN}",
"Notion-Version": "2022-06-28",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
def fetch_block_children(block_id: str, page_size: int = 100) -> list:
url = f"{BASE}/blocks/{block_id}/children"
params, results = {"page_size": page_size}, []
while True:
res = requests.get(url, headers=HEADERS, params=params)
res.raise_for_status()
data = res.json()
results.extend(data.get("results", []))
if not data.get("has_more"):
break
params["start_cursor"] = data["next_cursor"]
return results
def fetch_page_blocks_recursive(page_id: str) -> list:
def expand(block):
if block.get("has_children"):
kids = fetch_block_children(block["id"])
block["children"] = [expand(k) for k in kids]
return block
roots = fetch_block_children(page_id) # page 本身作為起點
return [expand(b) for b in roots]
paragraph → 純文字heading_2 → 標題文字code → 包含 language 與程式碼本身to_do → 附加 checked 狀態parse_learning_blocks.py 程式碼
def join_text(rich_text_arr):
if not rich_text_arr: return ""
out = []
for rt in rich_text_arr:
if "plain_text" in rt:
out.append(rt["plain_text"])
elif "text" in rt and rt["text"]:
out.append(rt["text"].get("content", ""))
return "".join(out).strip()
def parse_block(block):
btype = block["type"]
data = block[btype]
# 大多數型別都有 rich_text:heading_*、paragraph、bulleted_list_item、to_do…
if "rich_text" in data:
item = {"type": btype, "text": join_text(data["rich_text"])}
if btype == "to_do":
item["checked"] = data.get("checked", False)
if block.get("children"):
item["children"] = [parse_block(c) for c in block["children"]]
return item
# code 類型:取語言與內容
if btype == "code":
return {
"type": "code",
"language": data.get("language"),
"code": join_text(data.get("rich_text", [])),
"children": [parse_block(c) for c in block.get("children", [])] or None
}
# 其它型別先原樣保留(例如 divider、image…)
item = {"type": btype, "raw": data}
if block.get("children"):
item["children"] = [parse_block(c) for c in block["children"]]
return item
def parse_blocks(blocks):
return [parse_block(b) for b in blocks]
這支程式的主要目的,是把前面三支模組程式串成一條完整的流程,讓我們可以一鍵執行,直接從 Database 拉資料 → 抓 Page → 清理 Block → 輸出 JSON。
fetch_learning_database.py
rows 拿第一個 Page ID
fetch_learning_page.py
parse_learning_blocks.py
{
"type": "code",
"language": "python",
"text": "x = 5"
}
data/clean/page_blocks_learning.json
run_day6.py 程式碼
import os, json, collections
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from fetch_learning_database import query_database_all
from fetch_learning_blocks import fetch_page_blocks_recursive
from parse_learning_blocks import parse_blocks
load_dotenv()
DB_ID = os.getenv("NOTION_DATABASE_ID_LEARNING")
os.makedirs("data/clean", exist_ok=True)
rows = query_database_all(DB_ID)
print("Total rows:", len(rows))
all_pages = []
counter = collections.Counter()
for row in rows:
page_id = row["id"]
blocks = fetch_page_blocks_recursive(page_id) # 取齊所有 children
parsed = parse_blocks(blocks) # 轉成統一結構
all_pages.append({"page_id": page_id, "blocks": parsed})
counter.update([b["type"] for b in blocks])
out_path = "data/clean/page_blocks_learning.json"
with open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(all_pages, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"Saved: {out_path}")
print("Top block types:")
for t, c in counter.most_common(10):
print(f" - {t}: {c}")
以本次範例資料的執行結果,執行python src/run_day6.py,在 Ternimal 看到:
Total rows: 8
Saved: data/clean/page_blocks_learning.json
Top block types:
- paragraph: 161
- heading_3: 73
- bulleted_list_item: 71
- column_list: 54
- divider: 51
- code: 19
- heading_2: 10
- child_database: 9
- quote: 4
- numbered_list_item: 3
打開 data/clean/page_blocks_learning.json,內容會像這樣:
每個 page_id 底下有 blocks,而 blocks 有多個對應的 type 與 text 等資料。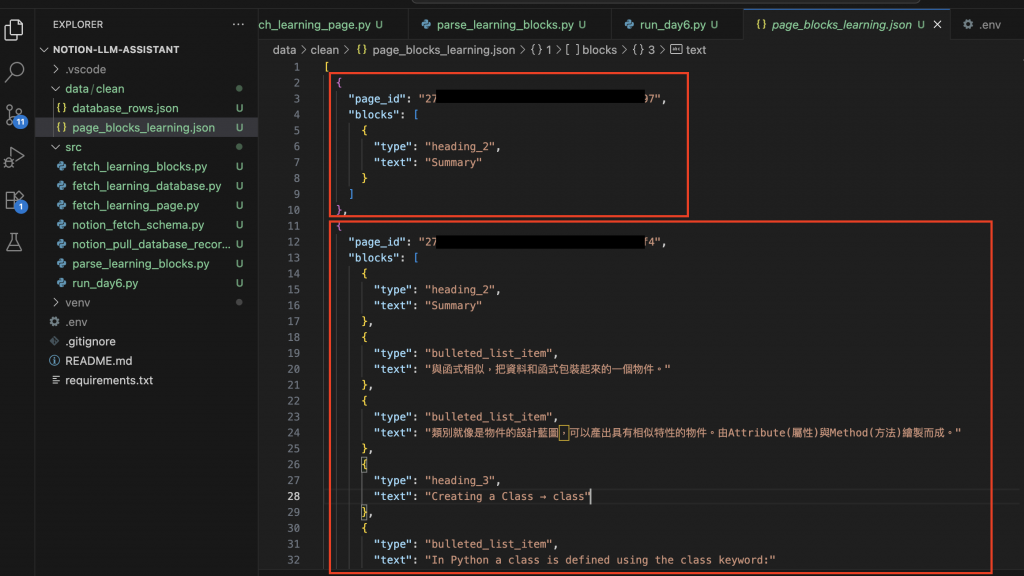
到目前為止,我們已經完成了幾個重要的里程碑:
Database rows,取得每一列對應的 Page ID,這是 Data Pipeline 的入口,讓我們知道有哪些「章節 / 頁面」需要進一步處理。Page API 與 Block API,把頁面內的筆記、段落、程式碼區塊都抽取出來。Block 解析成乾淨的 JSON 結構,方便後續使用。在 Day 7,我們會進一步把這些模組串成一條完整的 Pipeline:
