今日大綱
邏輯斯迴歸實作我以常見的鳶尾花(Iris)資料集當作範例,在機器學習開源資料集網站UCI,或是sklearn library都可以下載。獨立變數為花萼長度 (sepal length)、花萼寬度 (sepal width)、花瓣長度 (petal length)以及花瓣寬度 (petal width),單位為公分,而依變數為種類,總共有三個,分別為山鳶尾 (Iris Setosa)、變色鳶尾 (Iris Versicolor)以及維吉尼亞鳶尾 (Iris Virginica)。
很多人很容易把False negative與False positive搞混,在記的時候我是以預測值的角度去看,False negative就是預測值為0,False positive就是預測值為1。
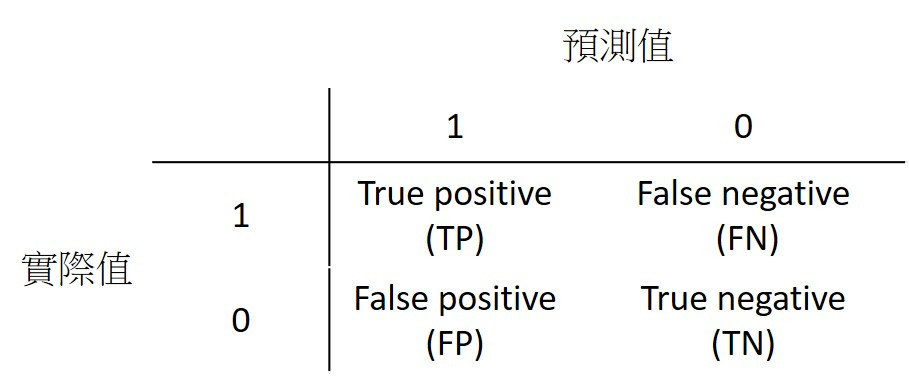
準確率 (Accuracy)
準確率為所有樣本中,預測正確結果所佔的比例。
準確率雖然越高越好,但並不一定適用於每個模型,如果1000筆資料中,負樣本數只有5筆,那模型將所有資料都預測為正樣本,準確率也高達99.5%。雖然這個例子較極端,但現實世界的資料大部分分布不均,正樣本或負樣本比較多。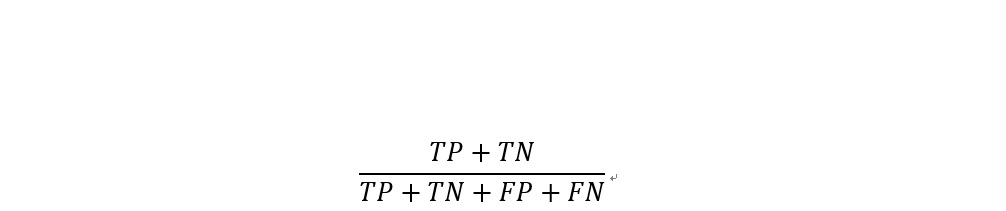
精確率 (Precision)
精確率為預測值為正的樣本中,正確預測為正樣本的結果所佔的比例。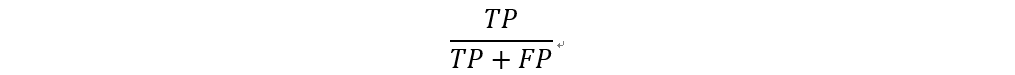
召回率 (Recall)
召回率為實際為正的樣本中,正確預測為正樣本的結果所佔的比例。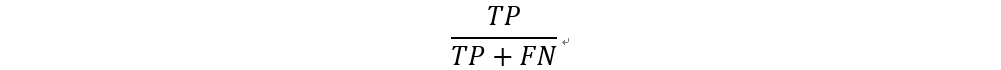
F1值 (F1-Score)
F1值為精確率與召回率的結合,用來衡量演算法表現好壞。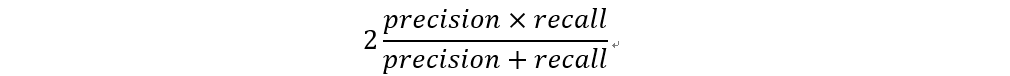
如果AUC等於0.5,代表模型效果與隨機預測相同,因此大部分以0.5當作判斷基準,如果高於0.5,代表模型具有預測效果;反之,分類器預測效果還比隨機預測差。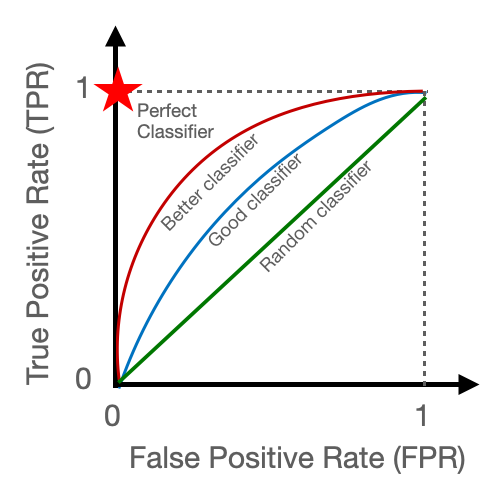
圖片來源:https://towardsdatascience.com/a-quick-guide-to-auc-roc-in-machine-learning-models-f0aedb78fbad
首先,將鳶尾花的資料匯入,資料型態為字典,印出資料集的敘述以檢視獨立變數與目標變數。
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = load_iris()
print(data.DESCR)
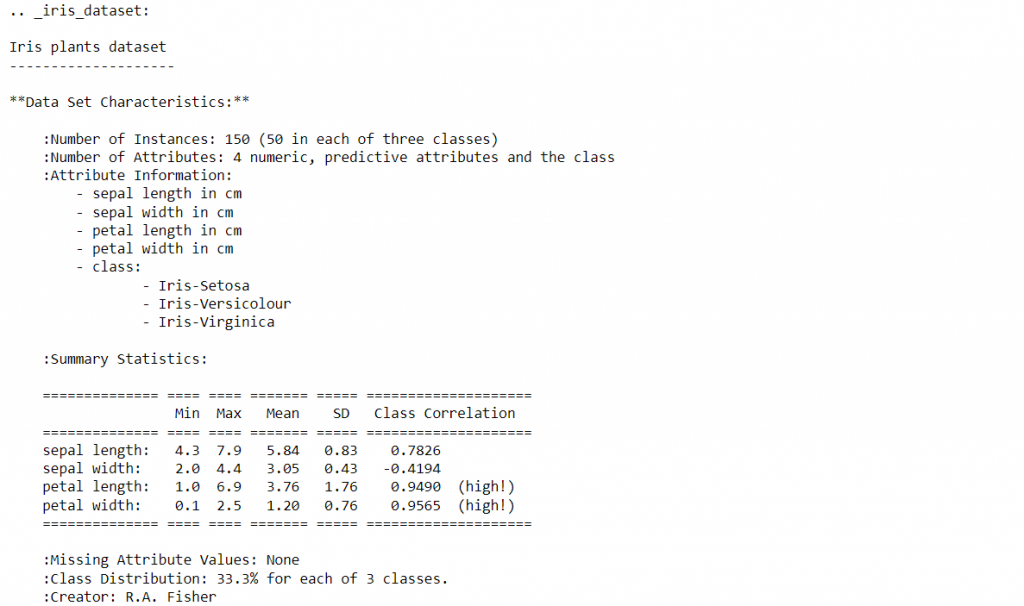
將資料存至x與y變數中,並且取出目標函數的名稱,總共有三個不同的鳶尾花品種
x = pd.DataFrame(data['data'])
#data的feature_names指定成x的column名稱
x.columns = data['feature_names']
y = data['target']
targets = data['target_names']
print(targets)
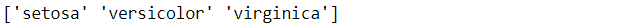
將資料切割成訓練集與測試集,進一步訓練Logistic regression模型,並且預測測試集裡的資料。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 1)
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(x_train, y_train)
prediction = classifier.predict(x_test)
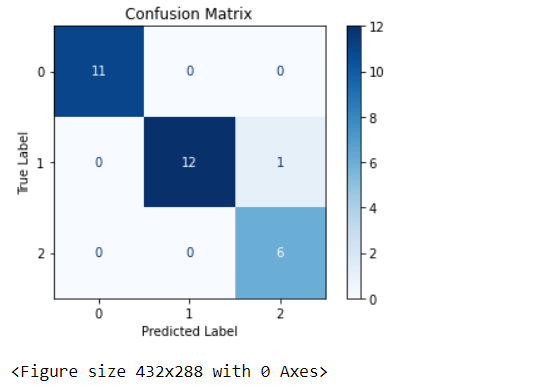
檢視模型的confusion matrix,從結果可看出僅有一個樣本預測錯誤。
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,prediction)
print(cm)

confusion matrix視覺化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import plot_confusion_matrix
color = 'black'
matrix = plot_confusion_matrix(classifier, x_test, y_test, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
matrix.ax_.set_title('Confusion Matrix', color=color)
plt.xlabel('Predicted Label', color=color)
plt.ylabel('True Label', color=color)
plt.show()
最後,呼叫classification_report即可輸出準確率、精確率、召回率以及F1-score
report = classification_report(y_test, prediction)
print(report)
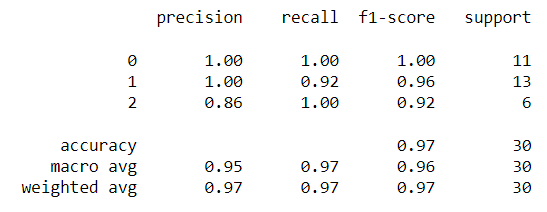
最後一行的support指的是每個類別擁有的總樣本數。
程式碼已上傳至我的Github
感謝您的瀏覽,我們明天見!![]()
